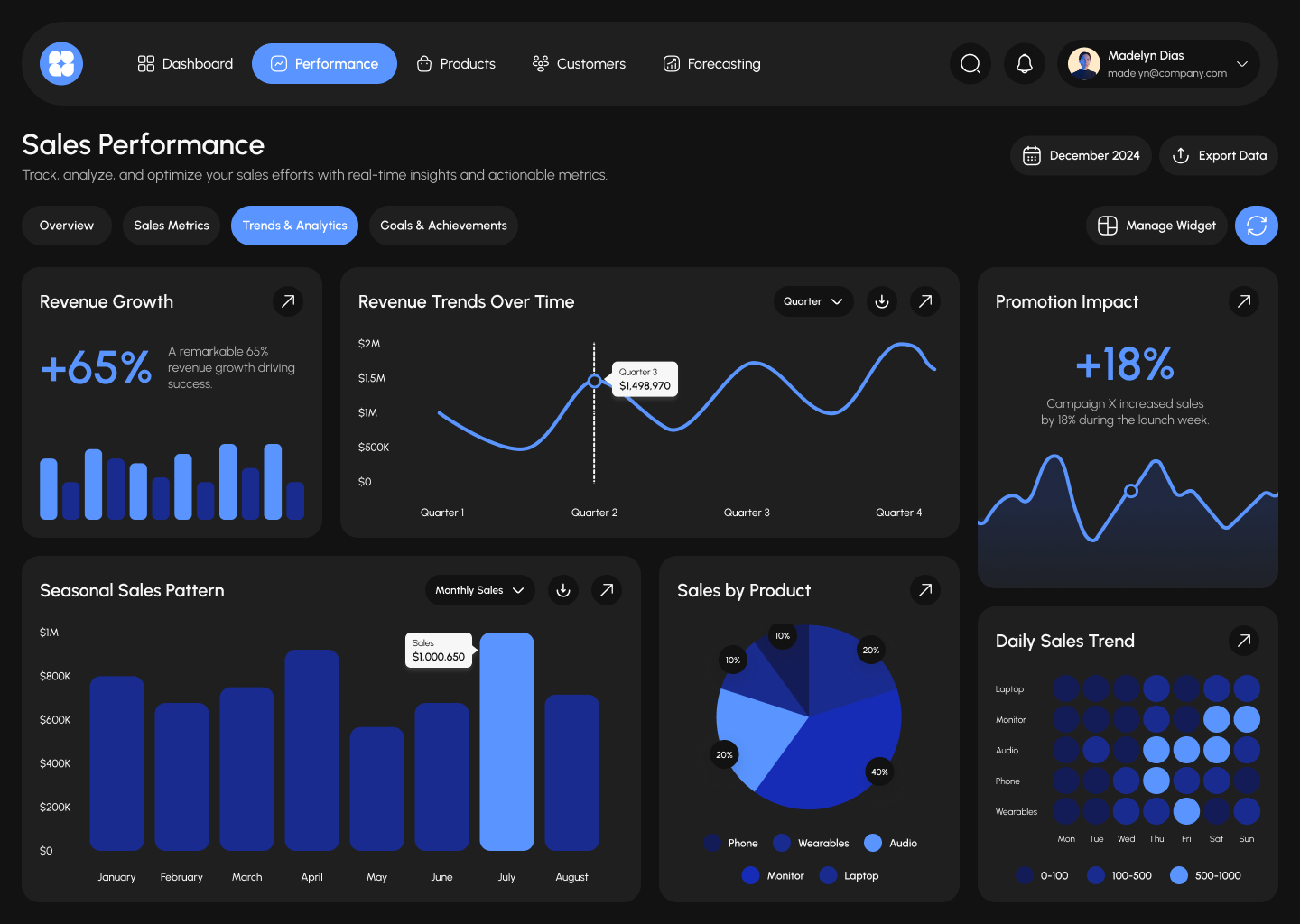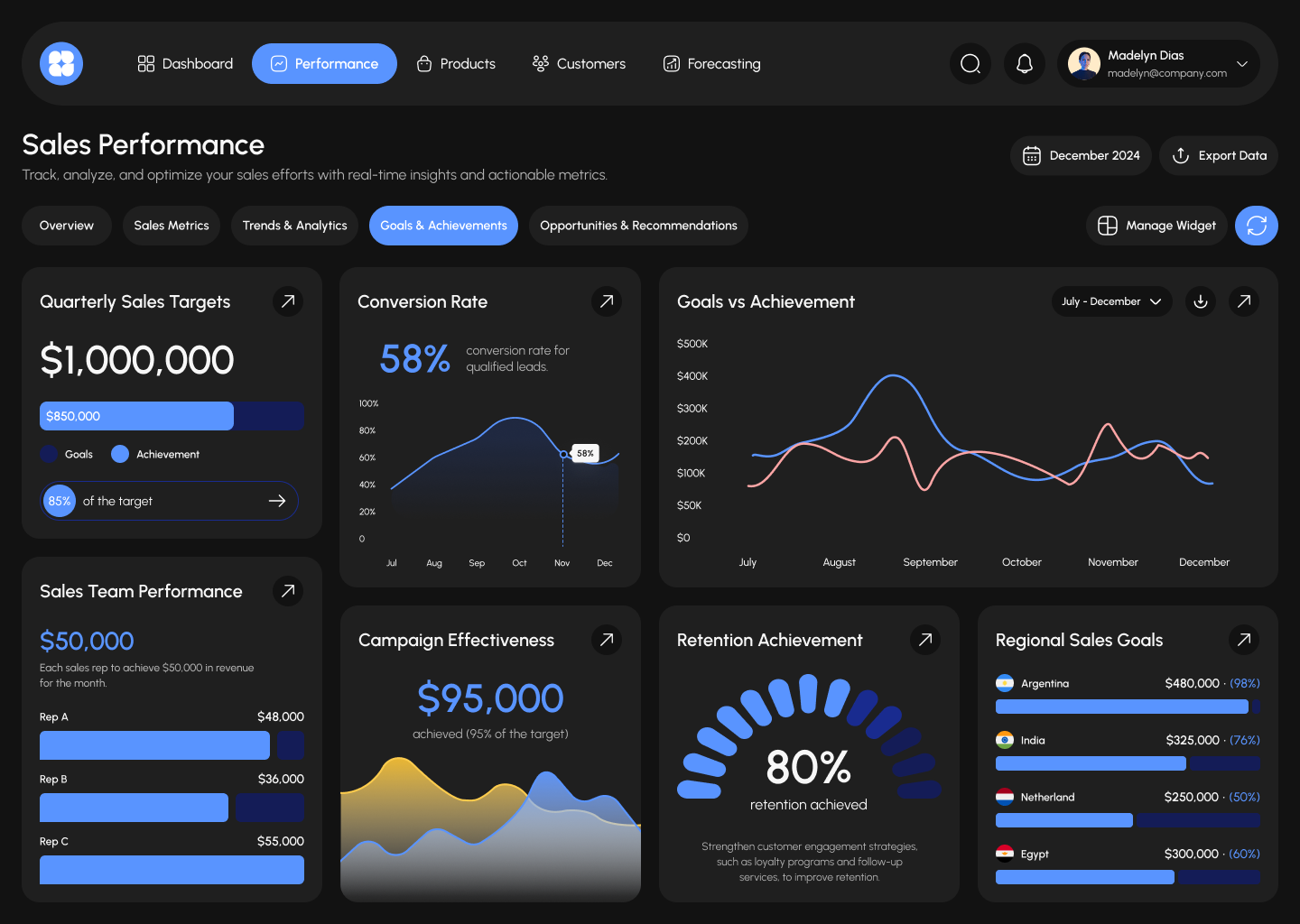





Advanced CRM Reports: Which Metrics Will Help Increase Sales?
Many companies still rely on simple Excel spreadsheets and dashboards when it comes to sales monitoring. But this approach quickly becomes ineffective: data is fragmented, manually updated, and doesn't provide a comprehensive picture.
To answer the key question of any business - how to increase sales - it's essential to see processes dynamically and understand where exactly customers are being lost. This is where CRM reports come in handy. They allow you to analyze every step of the funnel, manage your managers, and forecast results. With them, managers receive not just numbers, but a transparent picture: from the source of the lead to repeat purchases. This level of analytics makes it possible to develop strengths, eliminate weaknesses, and truly impact revenue growth.
In this article, we'll explore which advanced CRM reports can help boost sales, which KPIs are worth paying attention to, and how to interpret analytics to drive business growth.
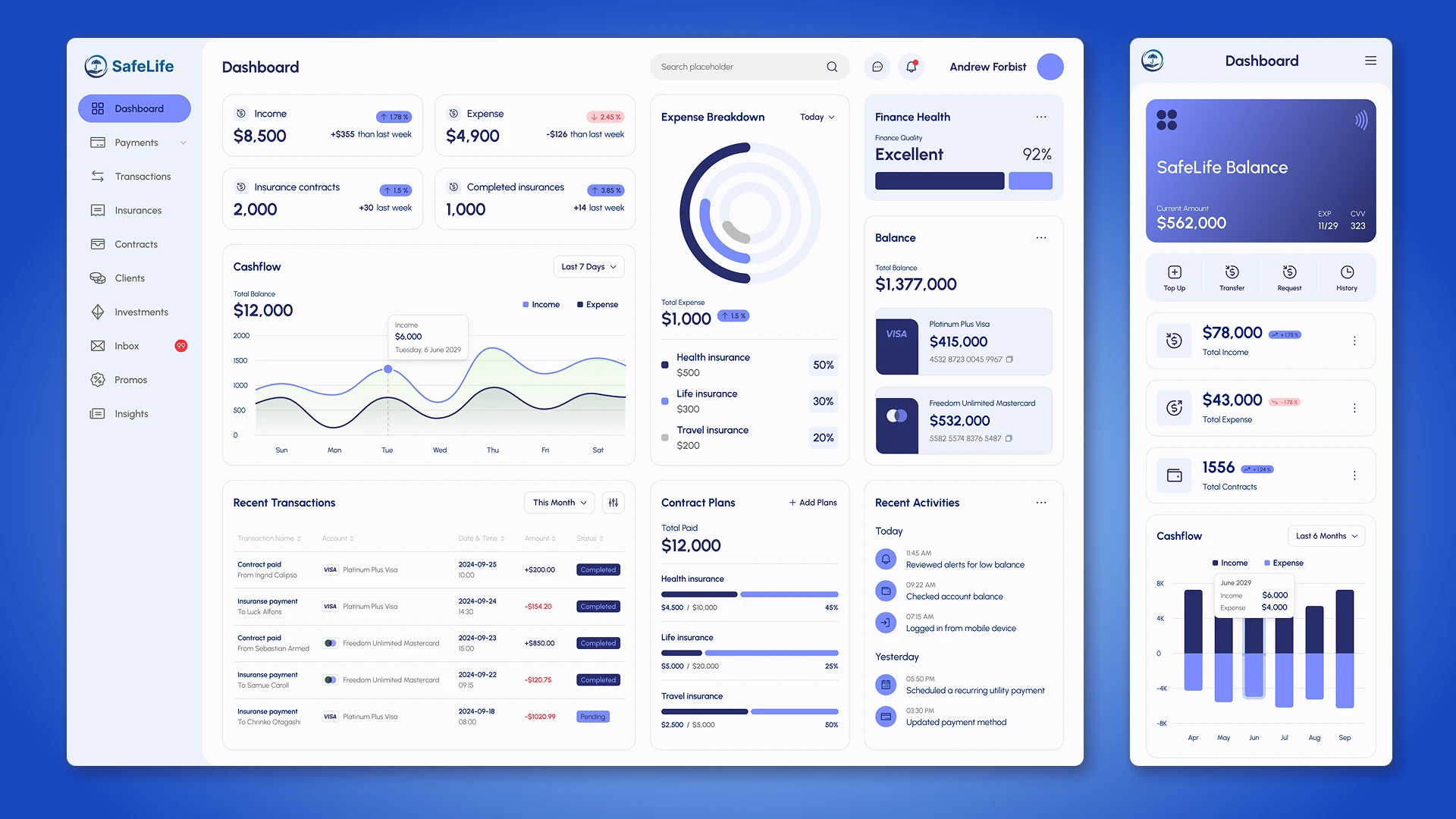
Business cycle of a transaction
What is a sales funnel?
A sales funnel is a model that describes a customer's journey from initial contact with a company to closing a deal. It clearly shows how many potential customers move from one stage to the next and where the business is missing opportunities.
Sales funnel (example):
- lead generation;
- first contact;
- presentation of a product or service;
- discussion of terms;
- conclusion of a deal.
This visualization helps businesses not only monitor the number of clients at each stage, but also identify growth points: which stages are "sagging," where the most leads are being lost, and how to fix them.
CRM sales funnel
The built-in sales funnel in the CRM automates this process. The system records every stage of customer interaction, from the first contact to the repeat purchase. Unlike manual accounting in spreadsheets, the CRM not only displays the status of each transaction but also collects analytics in real time.
What metrics can be tracked in a CRM funnel:
- number of leads at each stage;
- conversion between stages;
- average transaction cycle length;
- lead sources and their effectiveness;
- revenue forecast for open transactions.
Thanks to this, the manager sees not only a static picture, but also dynamics: where bottlenecks arise, how productive managers are, and which actions actually help increase revenue.
KPIs in sales
What are KPIs (Key Performance Indicators)?
Effective management requires relying on facts and figures, not just feelings. This is where useful metrics come in, showing how the business is performing. So, let's clarify the terms: KPIs, in simple terms, are key performance indicators- the numbers by which a business evaluates its performance. They help understand whether the team is moving toward goals: whether it's meeting its plan, whether resources are being used efficiently, and what could be improved.
Without key performance indicators, a company sees only "general figures"- for example, monthly revenue. But such data doesn't explain what specifically influenced the results. KPIs are essentially tools that allow for a detailed assessment of which processes are working effectively and which need adjustment.
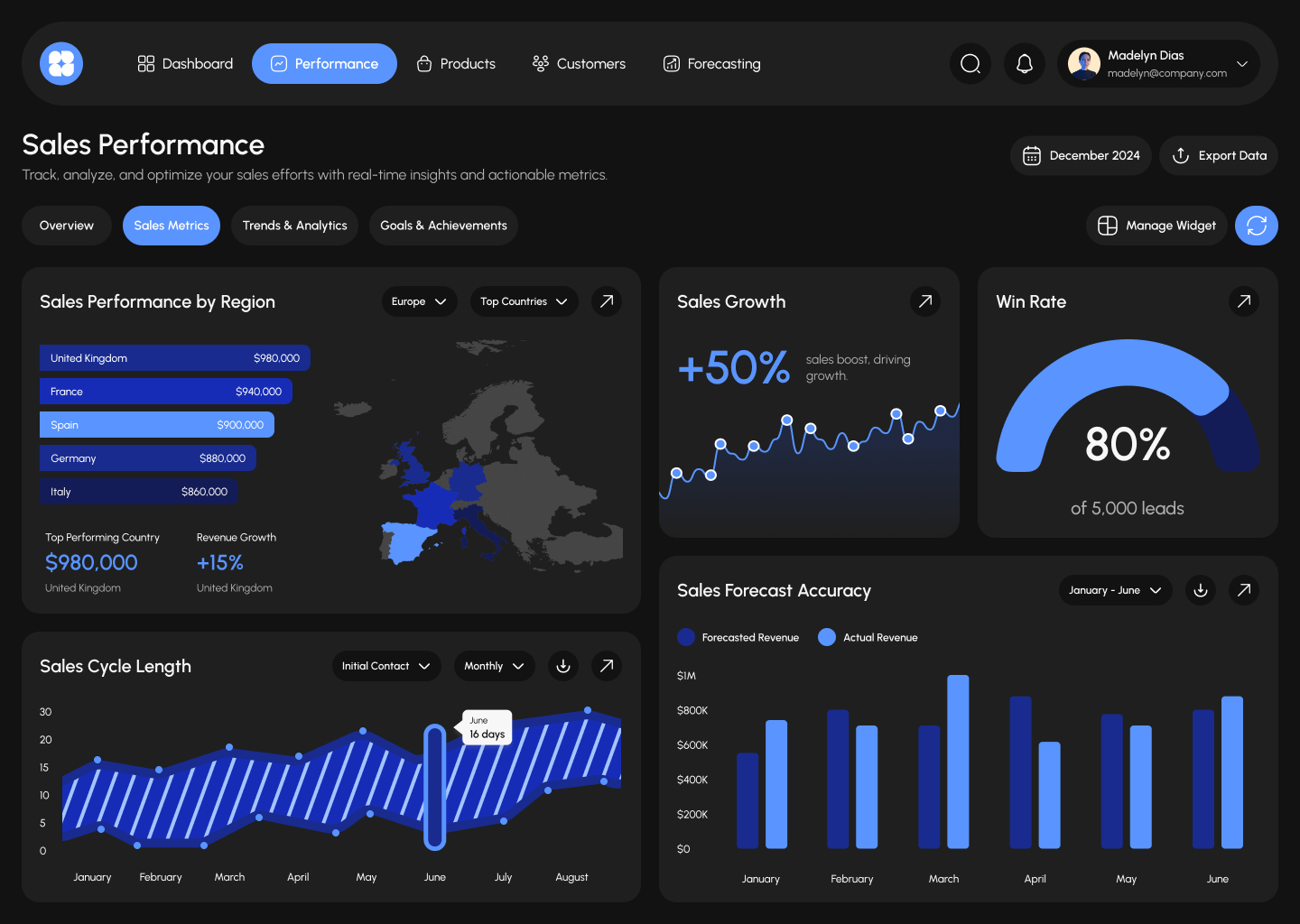
Key KPI metrics in sales
CRM can track dozens of metrics, but for most companies, the key ones remain:
- Conversion is the percentage of customers who move from one stage of the funnel to the next.
- Average check is the average transaction amount; it helps understand the value of each transaction.
- LTV (Lifetime Value) is the income a client generates over the entire period of cooperation.
- Cost per lead (CPL) is how much a company spends to acquire one customer.
- Repeat purchase rate shows how effectively a business retains customers.
Regular monitoring of these metrics through CRM reports helps identify weaknesses early and make management decisions based on data, not guesswork.
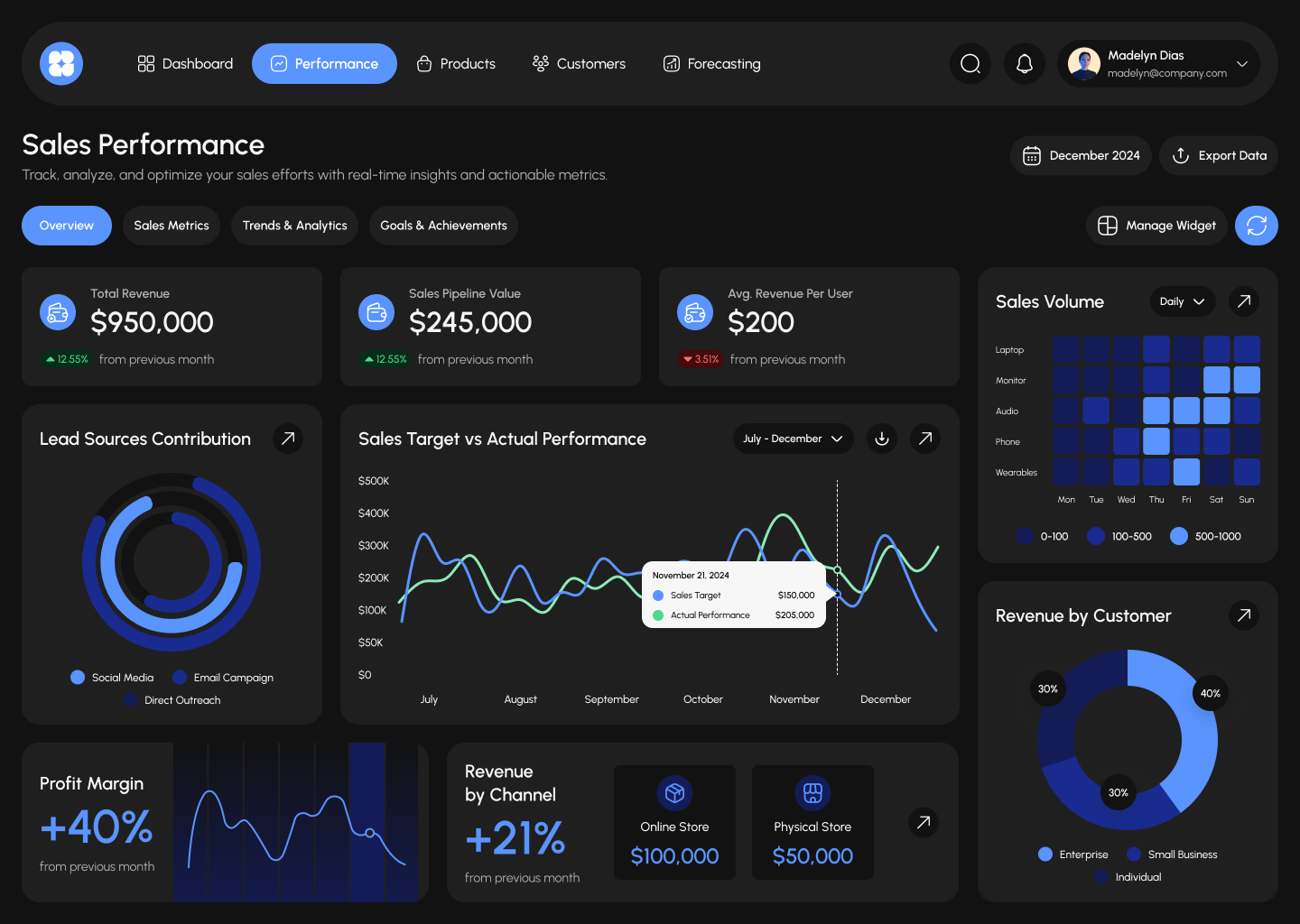
Analytics tools in CRM
An example of the integration of AvaCRM and Plausible
To ensure that management decisions are as accurate as possible, it's important for businesses to connect internal CRM data with external web analytics. This is the only way to understand not just "how many clicks there were on the website," but which channels actually bring in customers and impact commerce.
AvaCRM is a CRM system developed by our team. It's chat-based and runs as a PWA app, making it convenient for managers: they can communicate with clients, track deals, and access analytics directly from a browser or smartphone.
AvaCRM can be integrated with the Plausible system. This integration allows you to link traffic sources to specific deals and build a complete funnel view.
How does this work:
- Plausible tracks visits, channels, and user behavior on the site.
- Data is automatically transferred to AvaCRM.
- In CRM, the lead receives a “source tag” that is retained until the transaction is completed.
- The manager sees which channels and campaigns bring in customers, and which ones only generate clicks without conversion.
Practical benefits of integration:
- Determining the most effective advertising channels.
- Comparison of lead and conversion costs for each source.
- Linking marketing KPIs to real transactions, not superficial metrics.
This gives the company an end-to-end analytics tool: it can evaluate not only traffic but also its contribution to sales, adjust budgets, and strengthen the channels that are truly effective.
Interpretation of reports
Tips for reading CRM reports correctly
Even the most advanced CRM reports won't be useful if they're not interpreted correctly. For analytics to truly help a business increase sales, it's important to approach it systematically:
- Look at trends, not static numbers. The rise or fall of indicators over time shows how effective your actions are.
- Look for bottlenecks. If conversion drops sharply at one stage of the funnel, it's a sign of a problem that requires attention.
- Compare different segments. Divide customers by source, manager, or product to understand where churn is occurring.
- Make management decisions based on data. Analytics shouldn't just record results; it should help adjust commercial strategy.
Typical errors in interpretation
In practice, businesses often make mistakes that nullify the benefits of CRM reports:
- Focusing on just one KPI. For example, an increase in the average order value is encouraging, but if the number of transactions declines, overall revenue may not increase.
- Ignoring the entire sales funnel. Analyzing only final metrics (such as number of deals) hides problems at early stages.
- Lack of action on results. Reports alone don't change anything—implementing adjustments and monitoring their impact is key.
The key rule for interpreting reports is to look at the system as a whole and translate analytics into concrete management actions. Only then will data stop being "numbers for the sake of numbers" and begin to contribute to the company's growth.
Advanced reports for different business models
How to increase sales in a store
For offline and online retail, product-level detail is essential. Here, CRM reports help identify which items generate the most revenue and where growth potential lies.
Useful report examples:
- Best-selling products - what people buy most often, which categories are leading.
- Demand dynamics - how turnover changes during different seasons or promotional periods.
- Average order value - helps determine the effectiveness of upselling and cross-selling.
These reports allow you to adjust your product range, plan purchases, and more accurately answer the question of how to stimulate sales in a specific store.
How to Increase Sales in Small Businesses
For small companies, their most important resource is their people and acquisition channels. Therefore, CRM reports should focus on team effectiveness and customer retention.
Key reports:
- By managers - who closes more deals, who has a higher conversion rate.
- By acquisition channels - which sources provide "quality" leads, and which ones only provide traffic.
- By customer returns - how many customers return for a repeat purchase.
These metrics help optimize team and marketing efforts and focus on where they yield the greatest return.
Conclusion
Advanced CRM reports transform analytics from mere numbers into a practical growth tool. They help you not only see your current situation but also forecast future results, adjust your strategy, and identify new opportunities for revenue growth.
If you want more than a standard out-of-the-box solution, order CRM development and implementation of a customized analytics system from us, tailored specifically to your business needs.
FAQ
-
Is it possible to create your own KPIs and reports for your industry?
Yes, custom CRMs allow you to customize any metrics to suit your business. Contact us to discuss the first steps.
-
How often should KPIs be reviewed?
Regularly, at least quarterly. This helps us keep up with market changes and adapt our sales strategy.
-
Can CRM reports be used for sales forecasting?
Yes. This is especially effective if the system has accumulated a sufficient history of leads and deals. This data can be used to build forecasts and plan resources.
-
How do CRM reports relate to marketing?
CRM analytics allows you to see not only final transactions but also the effectiveness of acquisition channels. This helps you adjust advertising budgets and strengthen the sources that generate leads.
-
What reports does a manager need and what does a supervisor need?
The manager gets consolidated KPIs, sales dynamics, and the sales funnel. The manager gets detailed information on their deals, tasks, and clients. This approach allows everyone to see the data that helps them achieve their goals.