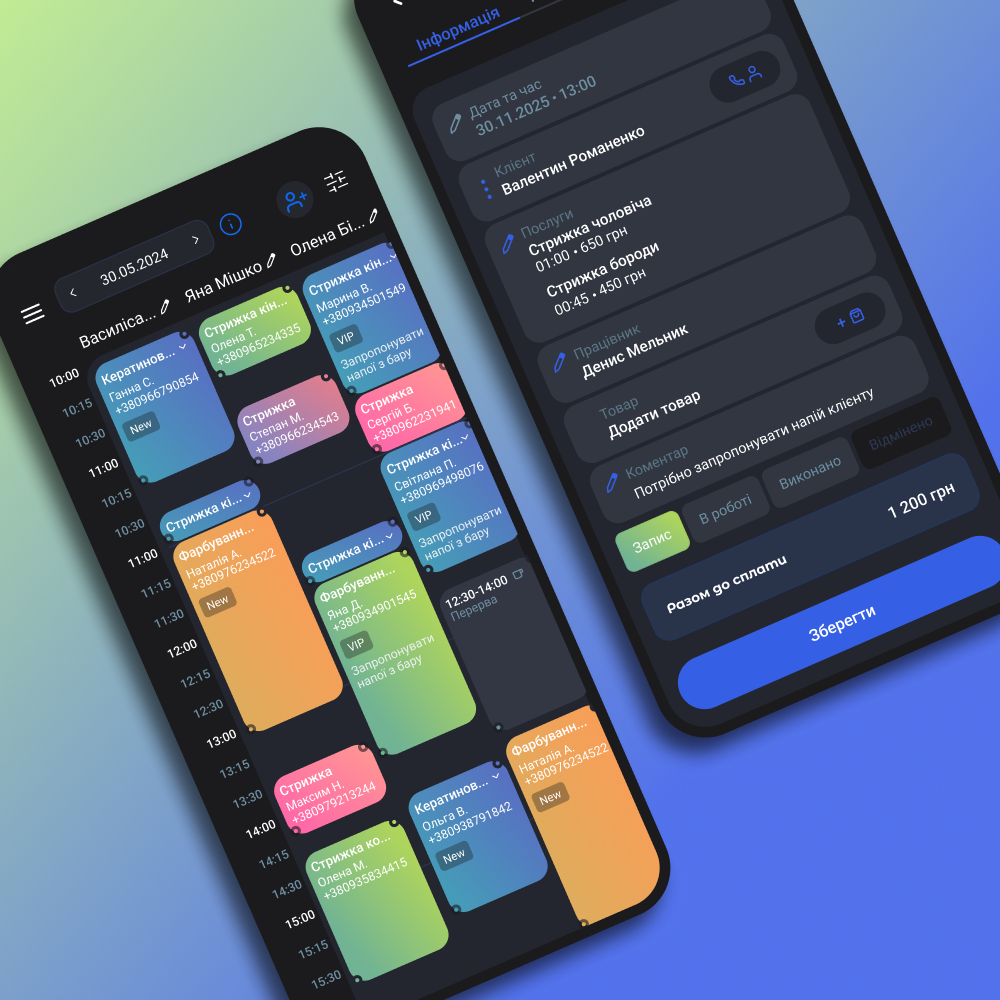





Today, businesses face an obvious problem: the volume of data is growing rapidly, and managing it manually or with standard CRM and ERP systems is no longer enough. Goods are lost in warehouses, production lines stand idle due to breakdowns, and managers make decisions based on guesses rather than facts. As a result, companies lose both money and time, falling behind competitors who act faster.
The solution lies in the Internet of Things (IoT).
Sensors, smart devices, and systems collect data and transmit it to an IoT platform or gateway, where the information is processed and then integrated with CRM and ERP systems.
This enables businesses to see the full picture “here and now”:
- track inventory without manual stock-taking,
- predict equipment failures,
- analyze customer behavior and generate relevant offers.
In essence, an IoT network transforms corporate systems from simple “accounting tools” into truly intelligent business management instruments.
Next, we’ll break down what the Internet of Things is, and how IoT integrates with business management systems, using examples from retail and manufacturing – from sensors and warehouse systems to logistics automation and quality control.
IoT: What Is It? The Internet of Things and IoT Networks
The Internet of Things is a concept where physical devices are equipped with sensors, software, and network connectivity. They can collect data from the environment, transmit it to accounting and management systems, and interact with each other without human involvement. This approach enables businesses to get the most accurate picture of what’s happening “here and now” and make decisions faster.
IoT in Simple Terms
Put simply, IoT is a network of “smart” devices: from temperature sensors in warehouses to cameras tracking the movement of goods. They send data to a central system, where the information is analyzed and used to manage processes. For example, a warehouse can automatically notify ERP about low stock levels, while CRM can alert a manager about reduced customer activity.
IoT Network: What Is It?
An IoT network is the infrastructure that unites all devices and sensors into a single system. It ensures real-time data exchange between equipment and management systems, making business processes transparent and controllable.
IoT Devices and Sensors: Why Businesses Need Them
The real strength of the entire system is that IoT sensors become the “eyes and ears” of a business, capturing data from the real world:
- RFID tags and readers – allow real-time tracking of goods and equipment.
- Cameras and computer vision systems – track object movements and help with quality control.
- Temperature, humidity, and vibration sensors – monitor storage conditions and equipment performance.
- Smart meters – collect data on resource consumption (electricity, water, gas).
As a result, companies receive an automated data flow without manual input, reducing errors, saving employees’ time, and enabling predictive management of processes – from warehouse logistics to customer service.
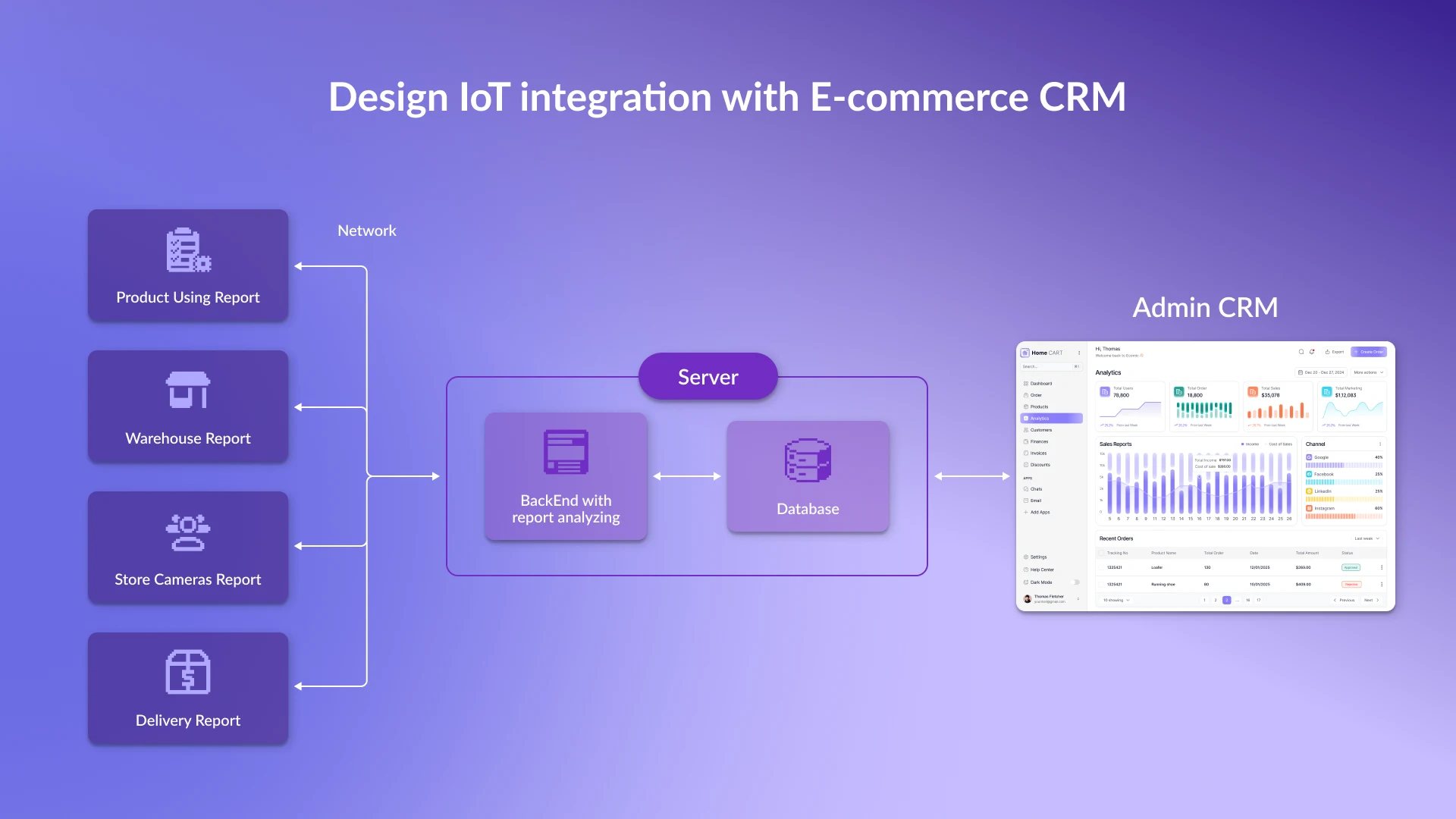
IoT Integration with CRM and ERP: Why It Matters
When business systems operate “disconnected” from real-world data, companies face delays, errors, and unreliable information. The Internet of Things in CRM and ERP solves this problem: devices and sensors transmit data directly into corporate systems, turning them into a “living” business management platform. This ensures process transparency, accelerates decision-making, and makes customer interactions more precise.
CRM and the Internet of Things: Personalizing the Customer Experience
CRM becomes much more effective when enriched with IoT data:
- Smart devices record customer behavior – for example, how often they use a product, which features are most in demand, or how equipment is operated.
- IoT data enables personalized offers – if a sensor shows that a printer cartridge is running low, the CRM system can automatically suggest a replacement.
- Marketing automation – based on device signals, CRM can trigger email sequences, notifications, or promotions without managers’ involvement.
In this way, CRM evolves from being just a “customer database” into a tool that predicts needs and builds loyalty.
ERP and IoT Networks: Transparency and Automation
For ERP systems, IoT integration opens new horizons:
- Real-time inventory management: warehouse sensors report stock levels, temperatures, and storage conditions.
- Equipment and production line monitoring: vibration and temperature sensors help predict failures and schedule maintenance in advance.
- Resource optimization: smart meters send data on energy consumption, helping cut costs.
- Logistics automation: RFID tags track goods along the supply chain, while ERP synchronizes this data with production and sales plans.
ERP receives data directly from devices and generates up-to-date inventory reports. In custom-built ERP systems, such modules can be tailored to the company’s specific processes for maximum efficiency.
As a result, ERP stops being merely an “accounting tool” and becomes the foundation of a “smart business,” where decisions are based on facts rather than assumptions.
IoT in Retail: Practical Examples
Retail is one of the sectors where IoT adoption is advancing most actively. Stores, warehouses, and logistics chains are filled with sensors that provide companies with new insights about customers and operations. This enables more accurate demand forecasting, an improved customer experience, and reduced operational costs.
Sensors and IoT Devices for Customer Behavior Analysis
With IoT, retailers can gain a deeper understanding of customer habits:
- Cameras and sensors record customer movement paths through a store, time spent at displays, and reactions to promotional zones.
- Smart shelves detect which items are frequently picked up but not purchased, helping optimize assortments.
- IoT data integrates with CRM, which automatically generates personalized offers and recommendations.
This helps increase conversion rates and strengthen customer loyalty.
IoT Solutions for Warehouse Automation and Inventory Management
IoT warehouse devices eliminate the need for manual inventory checks and reduce errors:
- RFID tags track the location of goods in real time.
- Sensors monitor storage conditions (temperature, humidity), reducing the risk of spoilage.
- Data from devices flows directly into ERP, where current stock reports are generated automatically.
A practical example is the Maraline online furniture store. To increase operational efficiency, we implemented a comprehensive solution:
- Integration with CRM automated order processing and customer database management, reducing communication time.
- Integration with warehouse systems ensured data synchronization and timely stock updates on the website.
As a result, customers always see accurate stock availability, while the company gains transparent inventory control – directly boosting customer trust and reducing operational risks.
IoT in Retail Logistics Management
IoT also supports retail logistics:
- GPS trackers and sensors on vehicles monitor cargo location and condition.
- The system automatically reports delays or route deviations.
- ERP synchronizes this data with supply and sales plans.
This reduces the risk of disruptions and optimizes the supply chain – from warehouse to end customer.
IoT in Manufacturing: Examples of Automation
Manufacturing companies benefit greatly from IoT integration with ERP: sensors and smart devices help monitor equipment, manage supplies, and ensure workplace safety. This reduces costs, minimizes downtime, and improves product quality.
IoT Sensors for Predictive Equipment Maintenance
One of the key applications of IoT in manufacturing is predictive maintenance. Sensors installed on machines and production lines track performance indicators (vibration, temperature, load).
- If parameters go beyond normal ranges, the system signals a potential failure.
- The ERP system processes the data in real time and creates a preventive maintenance schedule.
- This helps reduce downtime and extend equipment life.
As a result, production lines operate more stably, while repair and replacement costs decrease.
IoT in Logistics and Raw Material Supply Management
With IoT, companies can track raw materials and supplies across the entire supply chain:
- RFID tags and GPS trackers monitor transportation from supplier to workshop.
- ERP automatically updates data on incoming goods and current stock levels.
- The system predicts resource shortages and generates purchase orders in advance.
This makes the production process more flexible and resilient to disruptions.
IoT for Quality Control and Workplace Safety
IoT is also widely applied in quality assurance and workplace safety:
- Temperature and humidity sensors ensure proper storage conditions for raw materials and finished products.
- Gas, smoke, or toxic substance sensors monitor the safety of the production environment.
- Cameras and computer vision systems analyze products for compliance with quality standards.
Thus, IoT not only automates control but also enhances employee safety – which is especially important for large industrial enterprises. We implement such solutions in practice – you can explore more in our portfolio of completed projects.
Business Benefits of IoT
Integrating IoT with business systems is not just a “technical upgrade,” but a strategic move that directly impacts a company’s efficiency. Businesses gain not only new data but also the ability to make decisions faster, more accurately, and more profitably.
Key business benefits of implementing IoT include:
- Process transparency – management sees the real picture in real time: from equipment status to sales dynamics.
- Resource savings – automation of inventory management, energy consumption, and logistics reduces manual labor costs and minimizes the likelihood of errors.
- Faster decision-making – sensor data flows instantly into ERP and CRM, enabling immediate responses to business changes.
- Risk reduction – predictive maintenance and automated quality control minimize downtime and losses.
- Automation of core processes – this is where the Internet of Things shines most: from warehouse operations and logistics to customer service and product quality control.
- Service personalization – CRM enriched with IoT data can anticipate customer needs and offer solutions before the customer even asks.
- Increased loyalty – rapid responses to requests and relevant offers build trust and foster long-term customer relationships.
- Competitive advantage – companies that implement IoT adapt faster to market changes and deliver a new level of service to customers.
As a result, IoT becomes a key factor that enables businesses not only to optimize processes but also to stand out from competitors by creating a unique customer experience.
Conclusion
IoT, combined with business management systems, transforms corporate platforms from simple accounting tools into “smart” business management centers. In retail, this means warehouse automation, transparent logistics, and personalized customer experiences. In manufacturing, it means predictive equipment maintenance, quality control, and resource optimization.
IoT makes businesses faster, more transparent, and more efficient, helping companies cut costs and gain a competitive edge.
At AvadaCRM, we develop CRM systems with a wide range of integrations – from IoT sensors to ERP modules, chatbots, and e-commerce platforms. Want to implement IoT in your business? We’ll help adapt the solution to your needs and build a unified digital ecosystem.
FAQ
-
Can IoT be integrated into an existing CRM/ERP?
Yes. Integration is possible through APIs and custom modules that “connect” IoT sensors to corporate systems without requiring a full replacement.
-
Is IoT suitable for small businesses, or only for corporations?
IoT can be implemented gradually: from a few warehouse sensors or smart meters to complex systems integrated into ERP and CRM. This makes the technology accessible even for small businesses.
-
How does IoT affect the customer experience in online stores?
Thanks to IoT, customers receive personalized recommendations, real-time delivery tracking, and even support through chatbots that use IoT data.
-
Can IoT be combined with AI and analytics?
Yes. Most often, IoT works in tandem with AI: device data is used for predictive analytics, demand forecasting, anomaly detection, and process optimization.
-
Which industries, besides retail and manufacturing, use IoT?
IoT is actively adopted in healthcare (smart devices for patient monitoring), transportation (vehicle and cargo tracking), agribusiness (field and crop monitoring sensors), and energy (consumption tracking and optimization).