





CRM for banks
Banking services are a complex and demanding business segment. Furthermore, competition for clients in the financial sector is quite intense. Automating numerous daily processes with a CRM for banks will help you increase employee productivity and, consequently, reduce overhead costs. Another crucial component is customer trust and loyalty, which are especially difficult to achieve when it comes to financial matters. A CRM system is responsible for the bank's communication with its clients.
AvadaCRM develops CRM systems for banks that meet customer needs. You don't overpay for features you don't need, but you can always order them later with the option to integrate them into an existing system.
What is CRM for banks?
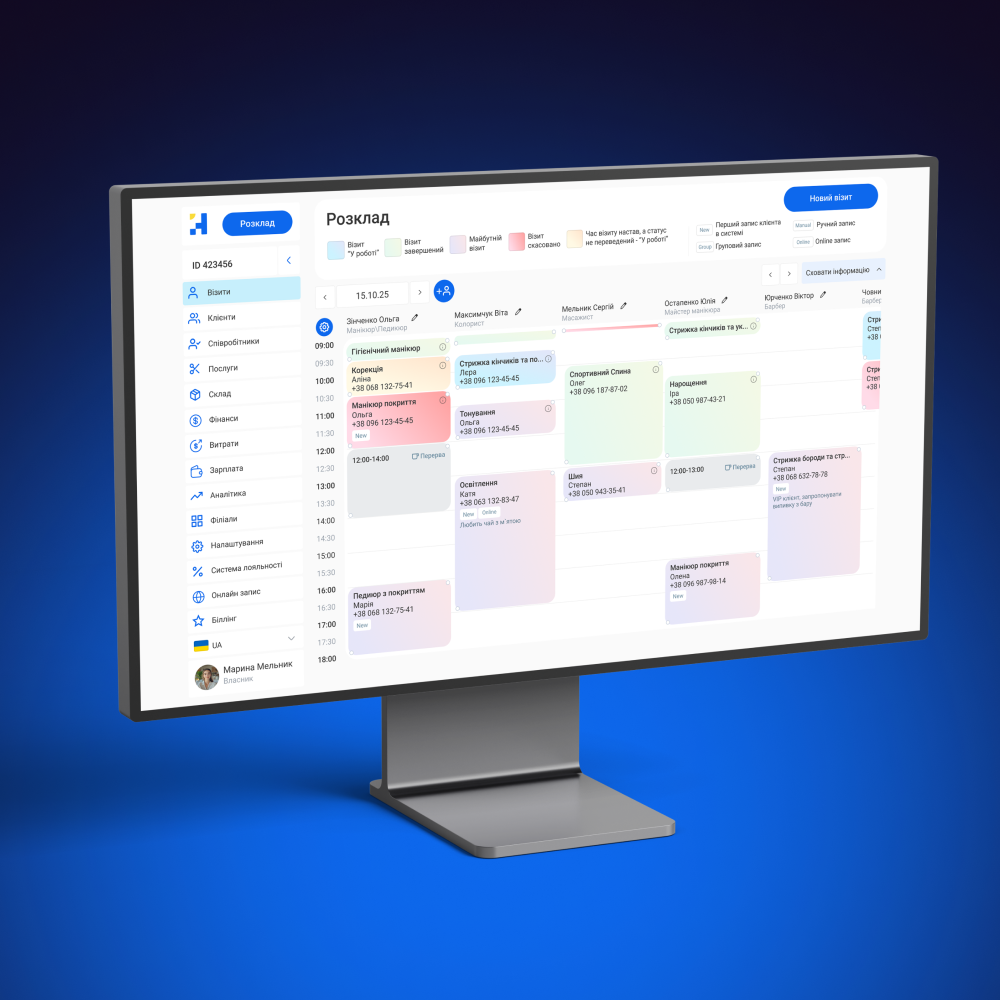
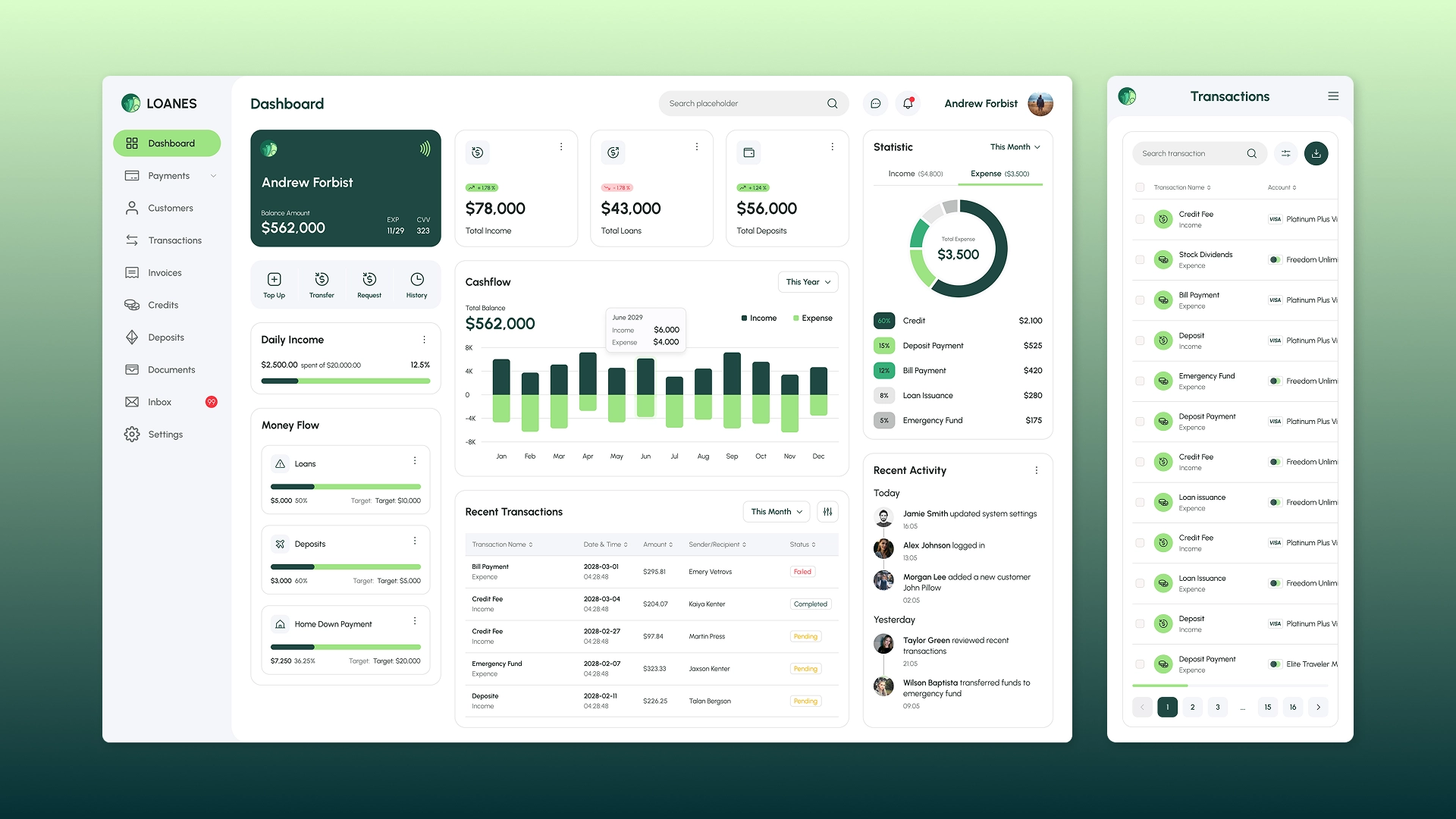
A CRM system for a bank is a specialized software solution for customer relationship management that integrates data on individuals and legal entities, products, transactions, requests, and communications across all channels.
Unlike general-purpose CRMs, a banking CRM takes into account the specifics of financial services: KYC and AML procedures, credit and deposit products, compliance control, and integration with core banking systems and other banking systems. Such a system becomes a unified digital core for customer service and sales.
CRM functions for banks
The CRM system for the banking sector includes a wide range of functional capabilities:
- A unified customer profile. Stores a complete history of interactions, products, transactions, and customer requests.
- Sales and product management. Automate sales processes for loans, deposits, cards, insurance, and investment products.
- Omnichannel communications. Integration with call centers, email, SMS, messengers, mobile apps, and web dashboards.
- KYC/AML and compliance support. Monitoring client checks, verification statuses, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Customer service automation. Manage requests, inquiries, claims, and SLAs.
- Analytics and reporting. Dashboards and reports on sales, customer activity, employee and branch performance.
- Integration with banking systems. Connection with core banking systems, scoring systems, payment gateways, ERP systems, and external services.
Stages of developing a CRM system for banks
Developing a custom CRM system for a bank is a complex, multi-layered process that requires in-depth financial expertise, an understanding of regulatory standards, and a high level of responsibility when working with data. The AvadaCRM team adheres to a transparent, systematic, and client-focused approach at every stage of the project.
1. Analysis and definition of automation goals
The first stage involves a detailed analysis of the bank's business processes, current IT infrastructure, and strategic goals. Specialists examine the specifics of working with retail and corporate clients, banking product sales processes, customer service, front- and back-office operations, call centers, and branches.
Particular attention is paid to KYC, AML, compliance, personal data protection, and the bank's internal regulations. This helps identify bottlenecks and growth areas, and formulate clear goals for CRM system implementation.
2. Formation of technical specifications
Based on the analysis, a technical specification - the key document of the project - is developed. The specifications outline the CRM's functional modules, user roles and access levels, employee workflows, and reporting and analytics requirements.
Integrations with core banking systems, payment systems, scoring platforms, ERP, and external services are also described in detail. A separate section is devoted to requirements for security, fault tolerance, performance, and scalability of the system. The agreed-upon specifications become the development roadmap and minimize risks at all stages.
3. Design and prototyping
After the technical specifications are approved, specialists design the CRM system architecture: they determine the logical structure of the modules, the interaction of components, the type of server architecture (monolith or microservices), databases, and integration methods.
Next, interactive interface prototypes are created in Figma, Axure, Adobe XD, or similar tools. Prototyping allows for early visualization of the future system, agreement on user scenarios, and adjustments before development begins.
4. UX/UI design development
The UX/UI design of the banking CRM is focused on employee convenience and speed. Interfaces are designed with user roles in mind: sales managers, call center operators, security personnel, analysts, and executives.
The design takes into account the bank's corporate style, brand book requirements, and modern interface standards. Particular attention is paid to navigation logic, minimizing manual interactions, and adaptability - the CRM should be user-friendly on workstations, tablets, and mobile devices.
5. Development of program code
The key stage is the implementation of the CRM system's software. Modern frameworks (React, Vue.js, Angular) are used for the frontend, ensuring high performance and a flexible interface. The backend is implemented in Python, Java, or Node.js using reliable PostgreSQL, MySQL, or MongoDB databases.
At this stage, integrations with banking systems are implemented via REST API or GraphQL, authorization and access control mechanisms, data encryption, tokenization, and security protocols (OAuth, JWT, etc.) are configured. The CRM architecture is designed to withstand the high workload and criticality of banking operations.
6. Testing and quality control
Before CRM implementation, comprehensive multi-layered testing is performed. QA engineers verify the correctness of the business logic, system stability, data security, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Functional, integration, and load tests are conducted, as well as fault-tolerance and user experience testing. The goal of this stage is to ensure uninterrupted operation of the CRM system even under high user activity and peak loads.
7. Release and implementation
The release phase includes deploying the CRM system on the bank's servers or in a secure cloud infrastructure, setting up domains, SSL certificates, and backup systems.
Data migration from existing systems, final field testing, and employee training are underway. CRM implementation is being carried out in stages to avoid disruption to the bank's current business processes and ensure a smooth transition to the new system.
8. Project support and development
Once launched, a CRM system requires ongoing technical support and development. The AvadaCRM team provides system monitoring, component updates, troubleshooting, and user support.
As the bank grows, the CRM system scales: new modules, integrations, analytics, and automation tools are added. This approach allows the system to remain relevant, secure, and maximally effective for the banking business.
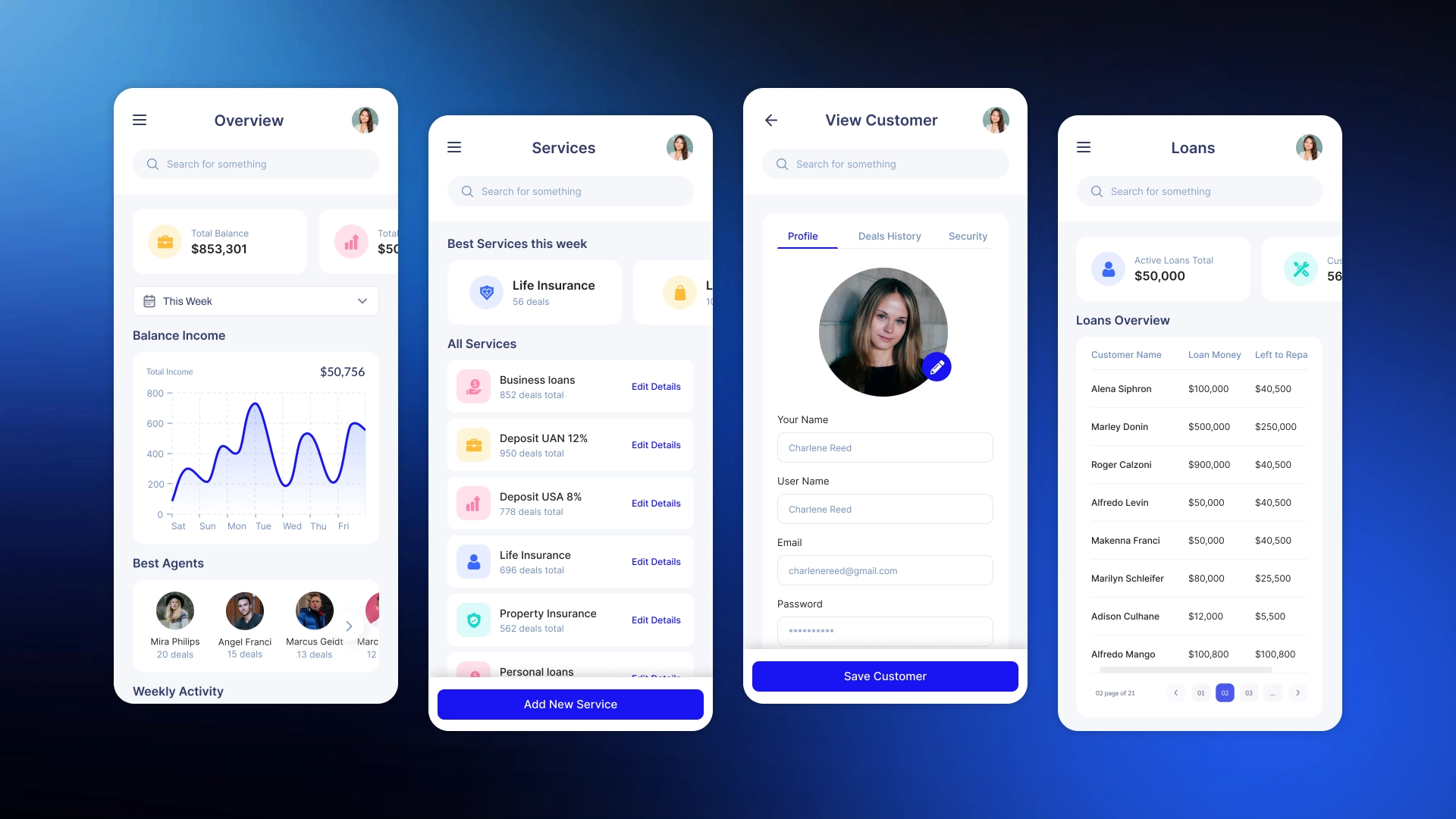
Why should you order a CRM system for your bank from AvadaCRM?
AvadaCRM specializes in developing customized CRM solutions for businesses with high security and scalability requirements. We create systems that are fully tailored to a specific bank's processes, rather than templated products.
Benefits of working with AvadaCRM:
- experience in developing CRM for the financial and corporate sectors;
- individual architecture according to the requirements of the bank and regulators;
- high data security and access control;
- deep integration with banking and accounting systems;
- the possibility of scaling and improving the system in the future.
Order CRM system development for your bank from AvadaCRM to improve customer service efficiency, accelerate sales and service processes, and gain a competitive advantage in the digital banking environment.