





CRM for manufacturing
Every manufacturing facility is a complex mechanism where planning inconsistencies, supply chain disruptions, raw material overruns, unfinished orders, and human error can slow down even the most promising project. In the age of digitalization, manual management of production processes makes a company inefficient and uncompetitive. That's why a CRM system for manufacturing isn't just a convenient tool, it's essential for effective growth and scalability.
With AvadaCRM, you'll find a reliable partner for your business's growth and development. We offer custom CRM development for manufacturing, which will become a key element in managing the entire production cycle.
What is CRM for production and sales?
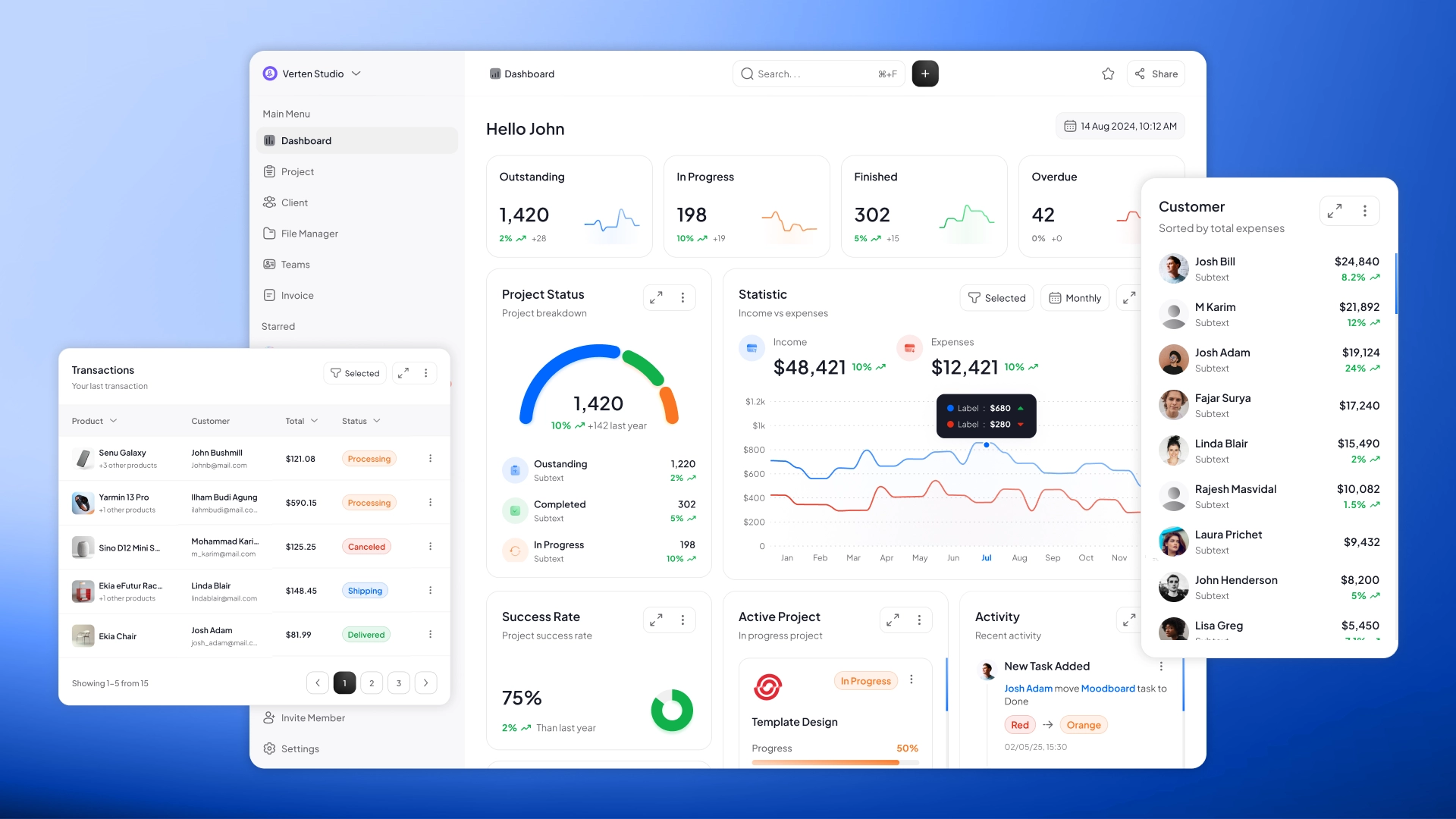
Enterprise CRM is a powerful ecosystem for order management, logistics and inventory control, quality control, HR management, and even production capacity analytics. It's a comprehensive software solution that allows you to digitize data, reduce costs, automate, and improve the transparency of core processes. Unlike traditional ERP systems, enterprise CRM focuses not only on internal processes but also on relationships with customers, suppliers, and contractors.
When automation of a manufacturing enterprise is needed
Automation is essential for every company that is growing, increasing volumes, and planning to scale. There are also a number of factors that point to the critical need for developing a CRM for production management, including:
- Due to the rapid growth in the number of orders, it is difficult to control their status, delays and confusion in priorities arise;
- Frequent errors and production failures caused by human factors, due to which documents are lost, tasks are forgotten, and deadlines are not met;
- the lack of an up-to-date picture of the warehouse's fullness leads to an overabundance of some materials and a shortage of others;
- difficulties with quality control and defects - when there is no transparent accounting, it is difficult to understand where deviations occur;
- problems with coordination between departments - planning, supply, production and logistics do not work smoothly;
- Lack of management analytics – it is difficult to quickly obtain accurate data on production, load, and profit.
Any of these factors hinders the growth of a manufacturing company. Therefore, developing a customized management system is not an expense, but a long-term investment in the company's development.
Benefits of implementing a production automation system
In a globally competitive environment, companies operating using outdated management methods risk losing not only their profits but also their market position. Therefore, modern manufacturing demands precision, efficiency, and speed. Full automation of production helps eliminate chaos in business processes, minimize errors, and create a transparent and manageable system. Let's take a closer look at the benefits of implementing a CRM system at your enterprise.
Optimization of production cycles
After implementing a CRM, a company can record and analyze every stage of the production cycle – from raw material receipt to finished product shipment. This allows for a clear picture of the company's operations, early identification of bottlenecks, and avoidance of delays. For example, industrial automation helps:
- reduce equipment downtime through forecasting and timely maintenance;
- speed up order fulfillment by automating production planning and resource allocation;
- make production more flexible to quickly reconfigure equipment to meet new orders;
- Avoid material waste and efficiently allocate production capacity thanks to modules for monitoring raw materials, labor, and equipment.
Automation of document flow
Applications, invoices, contracts, specifications, and other documentation are generated automatically in the CRM. This helps eliminate human errors, consolidate all documents in an electronic archive, and streamline processes such as auditing and certification.
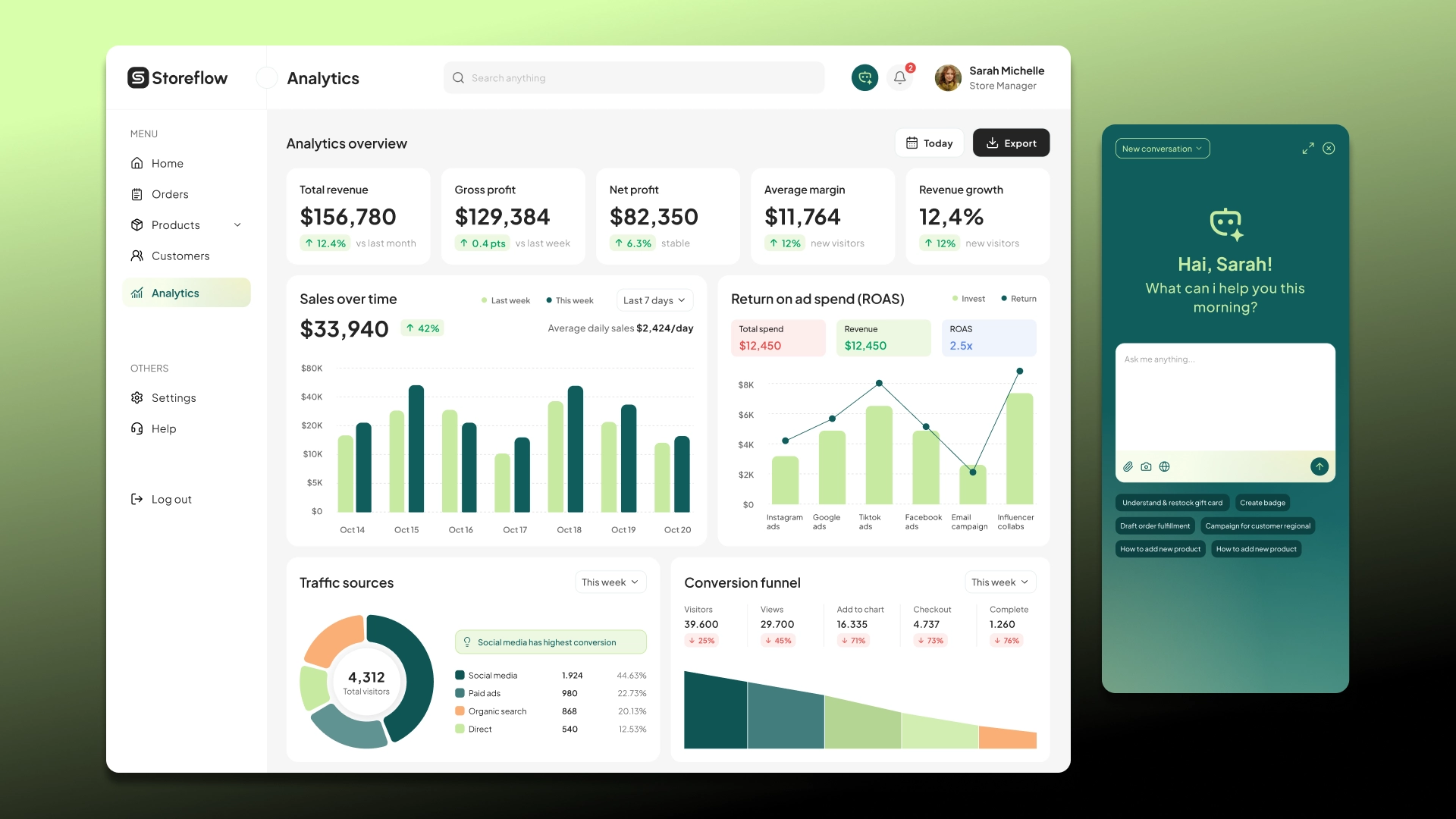
Intelligent planning
Comprehensive automation of production processes helps predict production line loads, account for seasonal demand, adjust delivery plans, and ensure on-time order fulfillment. This is especially important for companies with long supply chains.
Effective interaction with suppliers, customers and partners
CRM automates customer communications, data exchange with suppliers and contractors, tracks order statuses, sends notifications, and allows for interaction history for personalized service. Automating the company's production simplifies procurement and supply chain management, improving customer satisfaction.
Integration with other systems, equipment, and IoT
Modern production management systems can be connected to sensors on production lines to monitor machine status, assess their utilization, and alert when maintenance is needed, reducing the likelihood of unscheduled breakdowns. Furthermore, integration with other systems (ERP, MES, WMS) allows for the creation of a unified information space.
Optimization of material and inventory costs
Implementing a CRM system at a company allows for accurate accounting of materials and components, avoiding unnecessary purchases and reducing inventory. Automated production and logistics for material delivery reduces transportation costs, and monitoring expiration dates prevents the write-off of undamaged goods.
Improving staff efficiency
Automation of manufacturing facilities frees employees' time from routine processes to focus on more important and creative tasks, facilitating decision-making with real-time access to essential information. CRM also enables employee performance assessment.
Objectives of developing a CRM system for manufacturing
Developing a CRM for manufacturing has several key objectives, each of which is aimed at improving business efficiency and sustainability.
- Reduce operating costs and eliminate unnecessary links in the supply chain by automating routine processes such as order management, logistics, and data.
- Improve control at all stages of enterprise operations by receiving up-to-date information on raw material flow, order fulfillment, equipment loading, and personnel performance.
- Unite all departments of the company into a single ecosystem, creating a unified information environment and providing instant access to data. CRM for a manufacturing company reduces the risk of inconsistent actions between departments and improves management accuracy.
- Make informed strategic decisions based on reports on equipment performance, costs, order fulfillment times, and other key metrics.
- Manage your staff effectively – track employee workloads and assign tasks, automate payroll and bonus calculations, and evaluate KPIs.
- Minimize human error. Automating production processes reduces the likelihood of errors due to manual data entry, verbal agreements, or poor coordination between departments.
- Improve service and trust in the company. CRM for manufacturing companies integrates with email, messaging apps, and call centers, allowing for prompt responses to customer inquiries.
Which companies need automation of production processes?
Automating production processes is relevant for companies across a wide range of industries. Let's consider which industries benefit most from developing their own management systems:
- CRM for sewing production is necessary for optimizing warehouse stocks, managing fabric supplies, controlling product quality, and forecasting demand based on historical data;
- Automation of metallurgical production ensures control over all stages of raw material processing, accounting of consumables, and integration with ERP systems for precise planning and management of supply logistics;
- CRM for mechanical engineering is needed to manage complex production chains, monitor compliance with technical standards, and automate work with contractors and suppliers;
- Automation of the food industry helps control the expiration dates of raw materials and finished products, temperature control, manage distribution and interact with distribution networks, and monitor compliance with sanitary standards;
- The pharmaceutical industry management system ensures full control over production and product certification, compliance with regulatory requirements, and integration with warehouse and logistics management systems;
- In the production of building materials, automation of the production process helps optimize delivery routes and ensure quality control at all stages of production;
- A furniture manufacturing CRM manages material supply chains, records finished goods, automates assembly processes, monitors quality and delivery, synchronizes work with suppliers, tracks material balances in the warehouse, and allows for demand forecasting for different furniture categories.
Any manufacturing company seeking to reduce paperwork and accelerate data exchange should consider developing a CRM system for manufacturing.
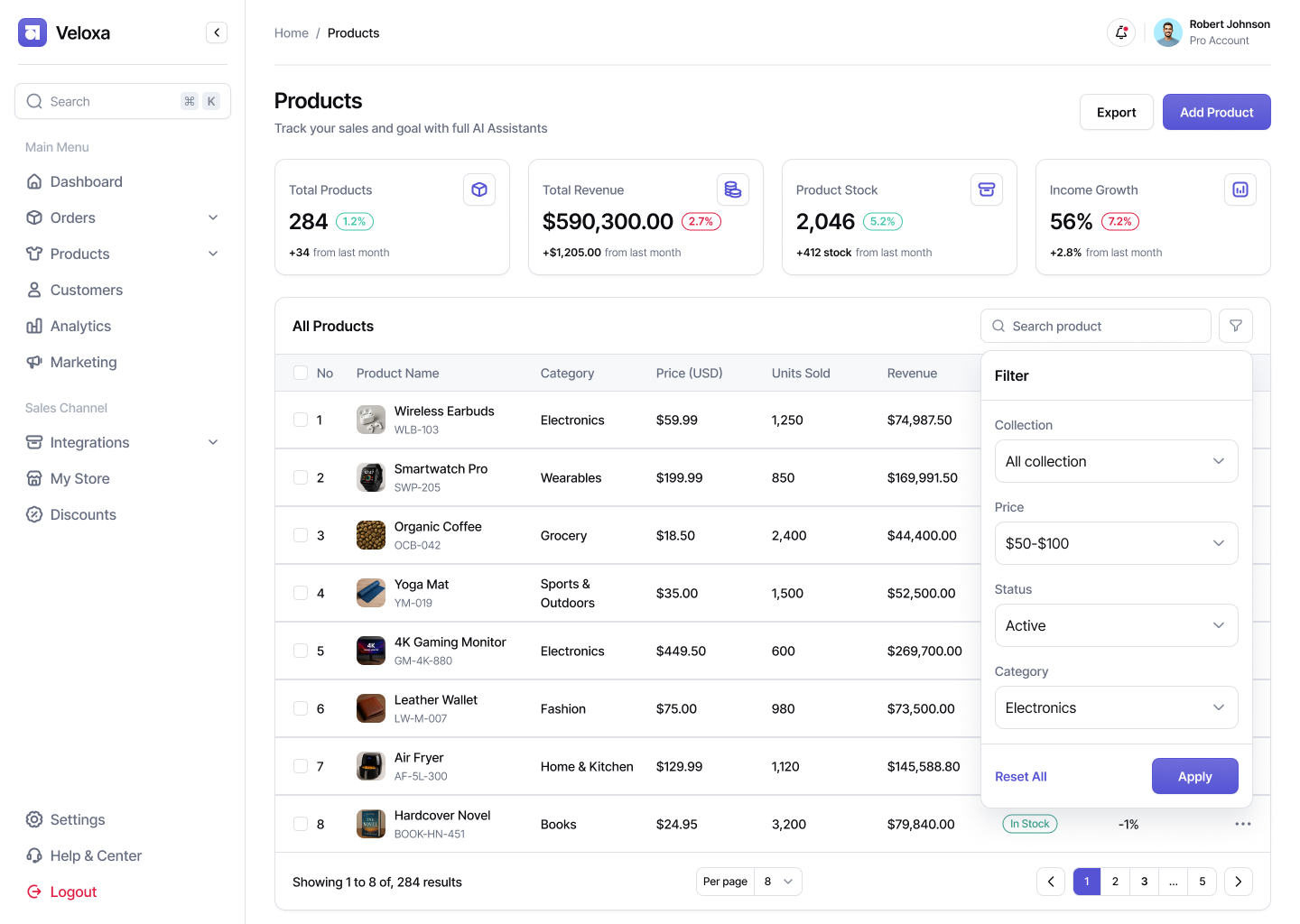
Functions of CRM systems for manufacturing enterprises
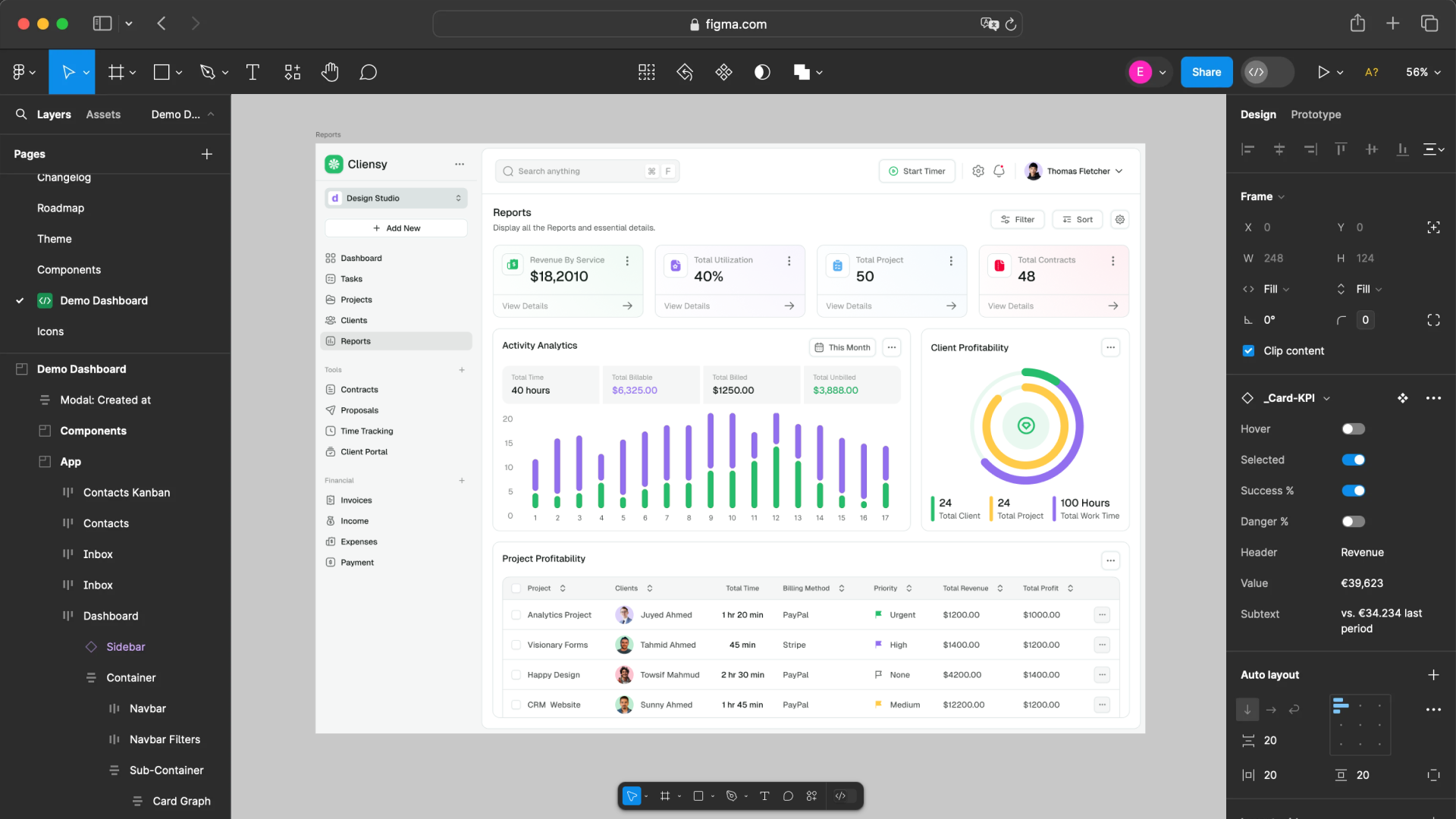
A customized CRM for a manufacturing company covers all stages – from order receipt to customer delivery. It may include modules for the following functions.
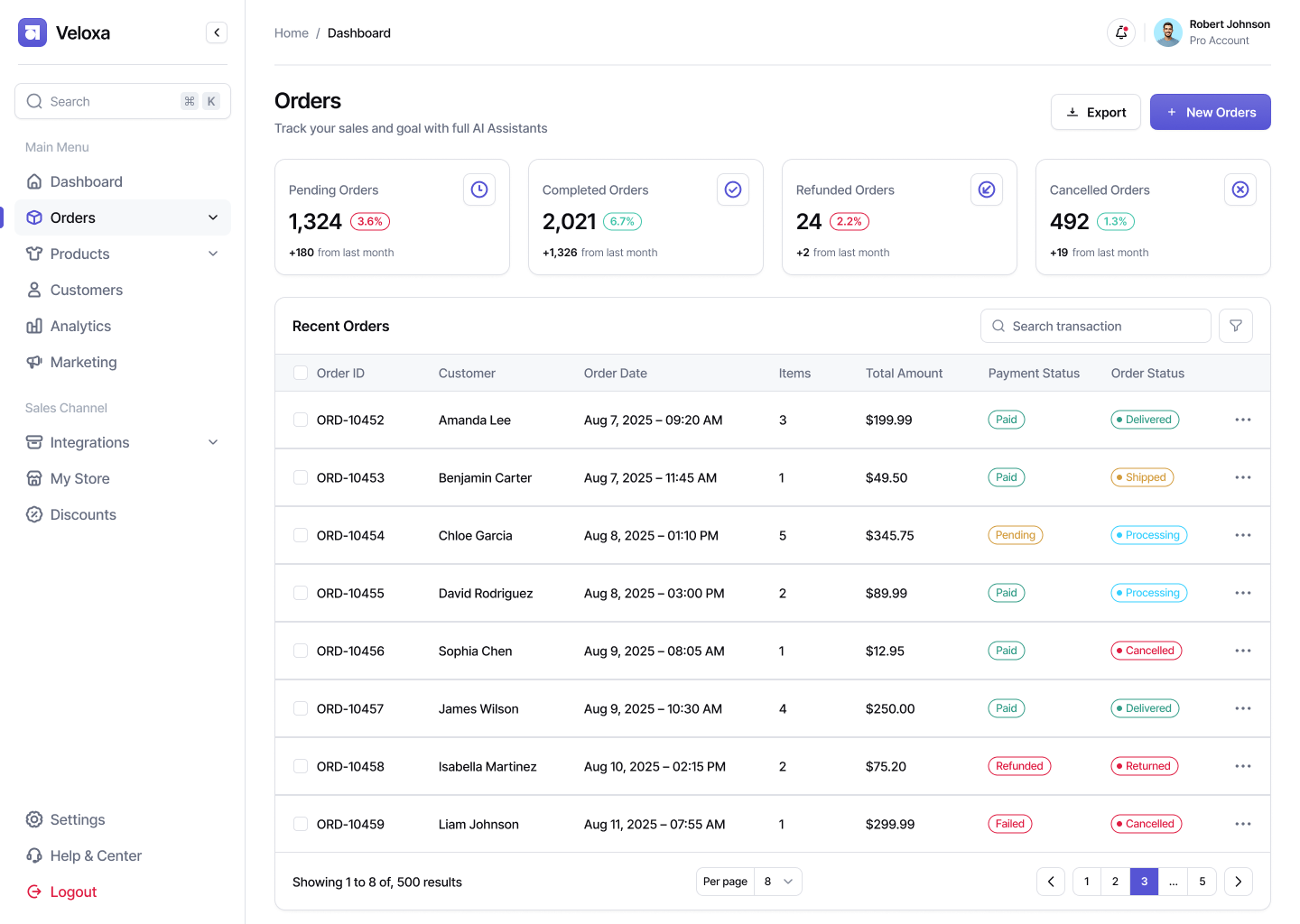
Production Order Management:
- creation of order cards based on customer requests;
- linking to nomenclature, technical documentation and route maps;
- control of deadlines, statuses, responsible persons and stages;
- visualization of production line loading;
- integration with an ERP system or accounting (e.g. 1C, BAS).
For example, a furniture manufacturing plant receives an order for a kitchen set. The system creates the order, assigns a unique number, attaches the drawings, and monitors the order's progress through the stages: cutting, assembly, and packaging.
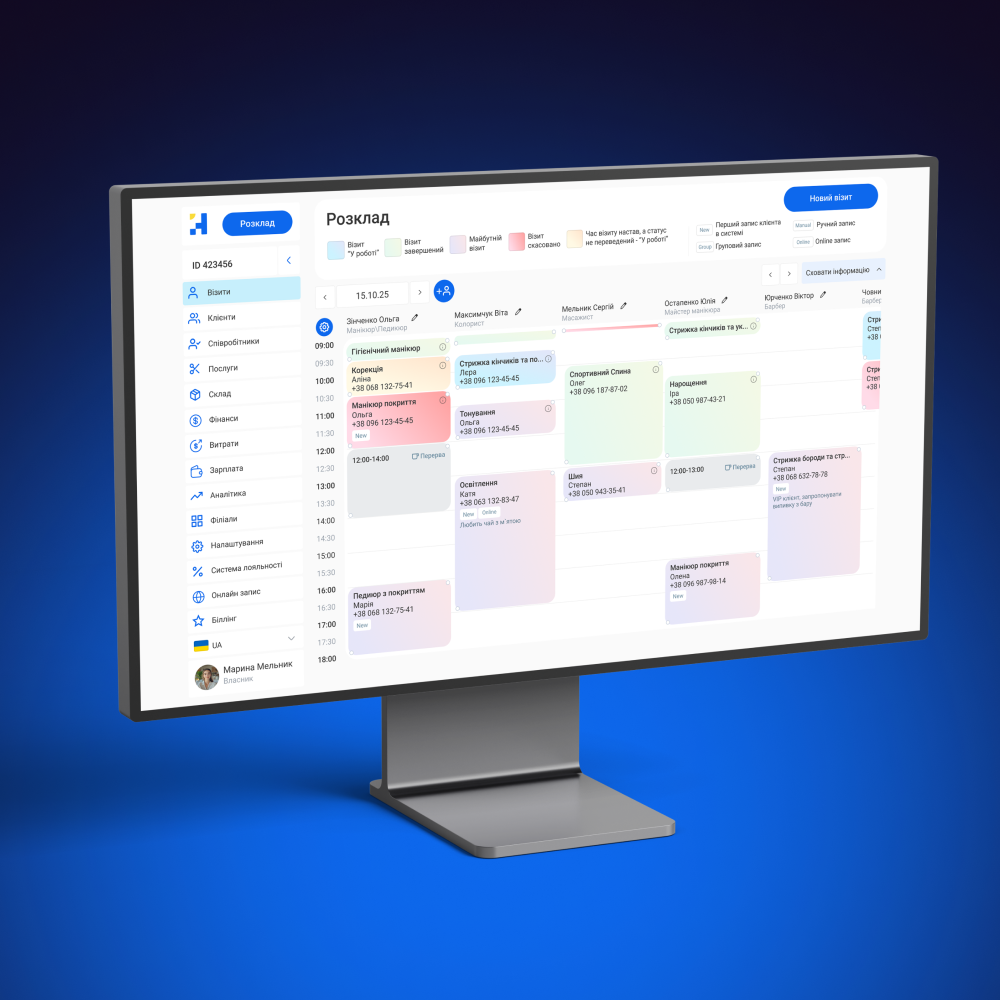
Planning and control:
- calendar-network planning (for example, using a Gantt chart);
- flexible distribution of orders across shifts and sections;
- taking into account the availability of personnel, equipment, and raw materials;
- Possibility of manual adjustment and automatic recalculation;
- support for multi-level production (semi-finished products, processing stages).
For example, a printing house's CRM generates a weekly plan, distributing tasks between shifts based on machine availability. If one of the lines breaks down, the system automatically reschedules the schedule and notifies the technician.
Quality control:
- built-in checklists and control operation templates;
- photo and video recording of defects, their classification;
- internal defect and complaint logs;
- reports on deviations and their causes;
- feedback to the technology department.
For example, when a packaging defect is detected, the CRM for the food industry records it in a photo, automatically creates an internal complaint, and notifies the technologist.
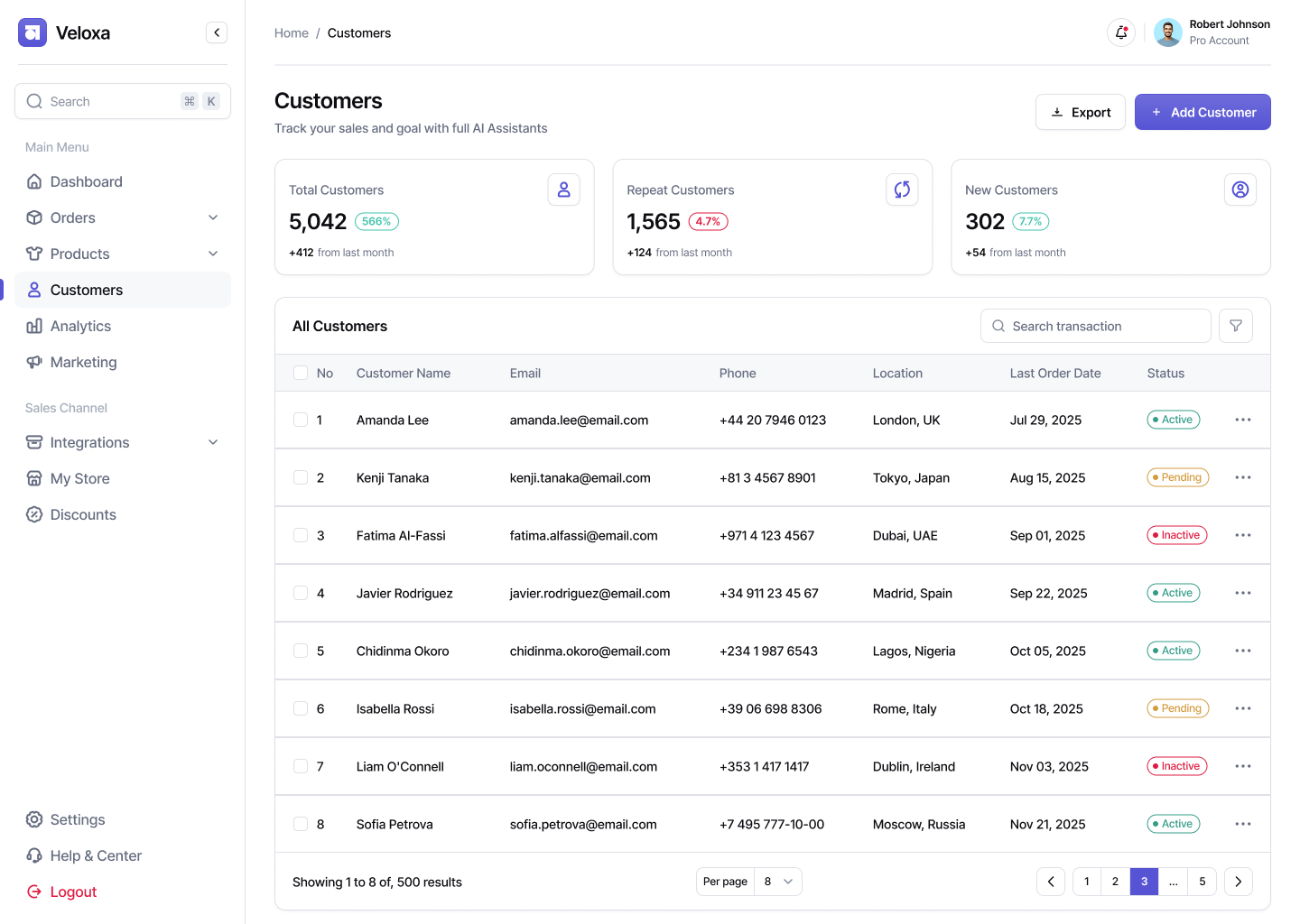
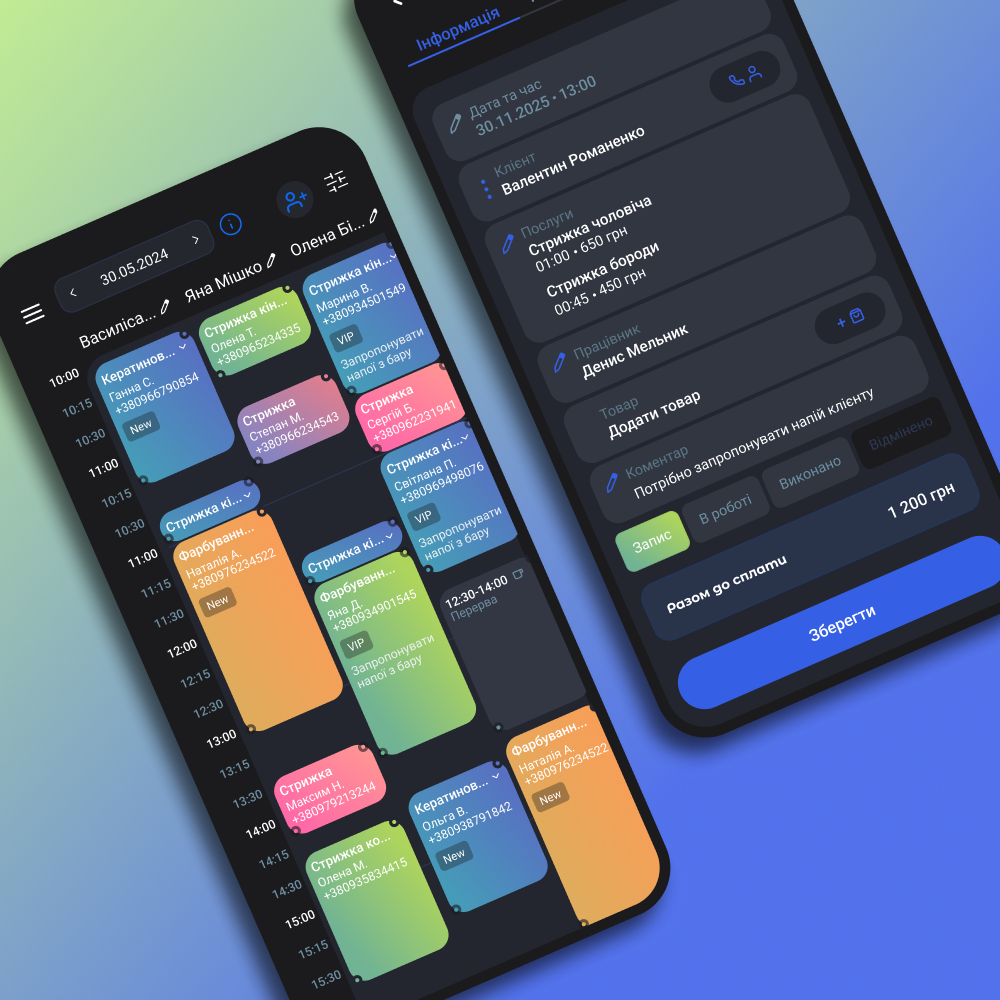
Personnel management in production:
- formation of shift schedules and monitoring of their compliance;
- distribution of tasks among employees and areas;
- control of loading, productivity, output;
- motivational modules and KPI calculation;
- recording violations of discipline and safety.
For example, a foreman sets a sewing plan for a shift. At the end of the shift, the sewing CRM calculates the output of each seamstress, taking into account the complexity of the item.
Warehouse and raw material inventory management:
- accounting of warehouse balances by batch, expiration date, and supplier;
- automatic calculation of the need for raw materials and materials for orders;
- reservation of raw materials for specific planned tasks;
- support for barcoding and mobile data terminals;
- integration with procurement and suppliers.
For example, if a production facility receives a large order for pipes, the CRM for a metallurgical plant checks the availability of the required diameters in stock and automatically generates a purchase order for the missing materials.
Financial module:
- calculation of the cost of each order;
- control of costs for raw materials, wages, depreciation;
- comparison of planned and actual profit;
- generation of acts, invoices, consignment notes;
- synchronization with accounting, banking, tax reporting.
For example, when analyzing the cost of a batch of drugs, a CRM for a pharmaceutical company will show a 10% overrun of packaging, help analyze all possible causes, and suggest ways to eliminate them.
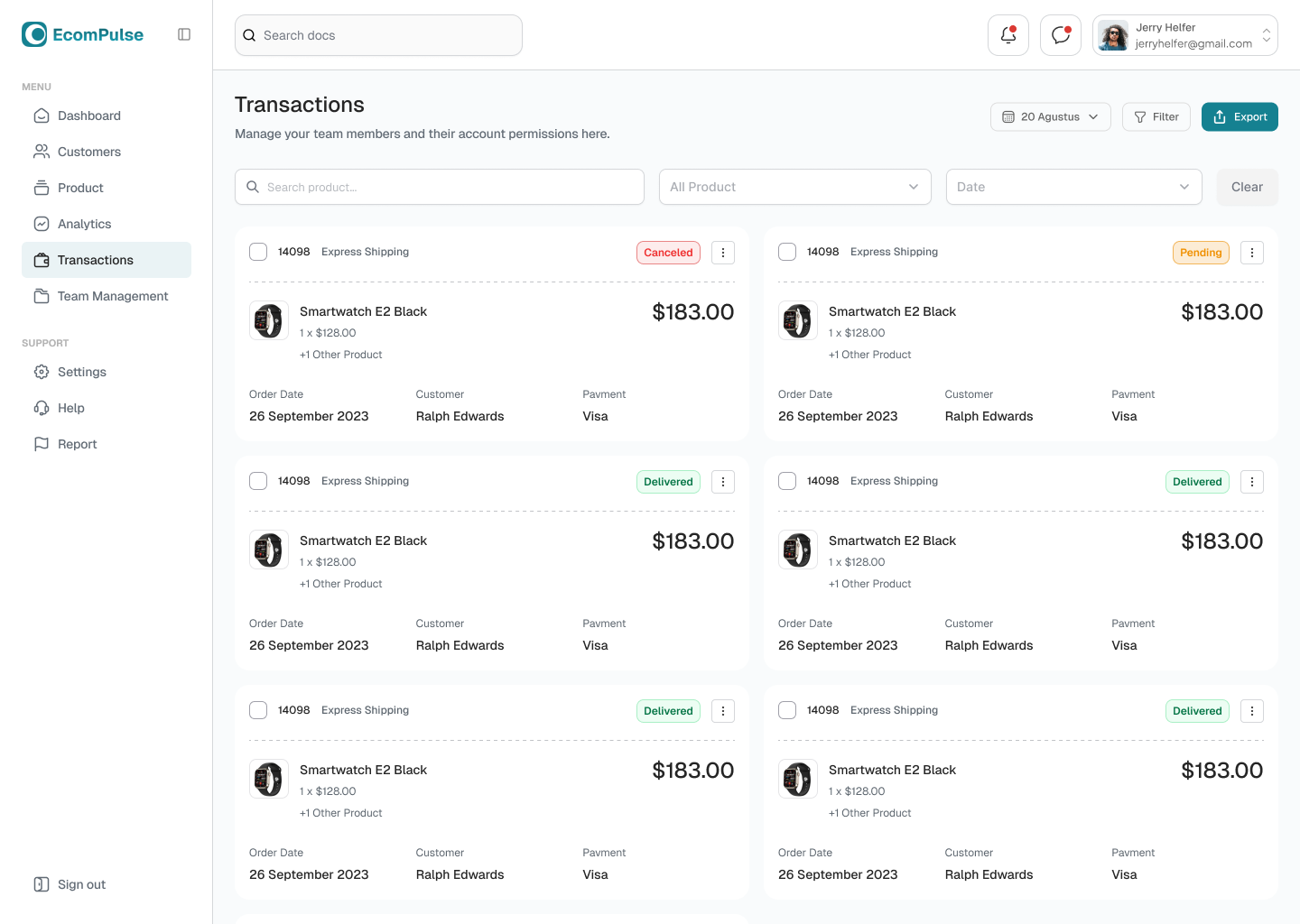
Logistics and shipping:
- management of internal and external logistics tasks;
- formation of shipping documents;
- optimization of delivery routes and integration with TMS;
- integration with courier services and transport companies;
- control over the implementation of logistics KPIs.
For example, when a window manufacturer creates a shipment for a customer in another city, a CRM for the window business automatically distributes orders across shipments, prints invoices, and calculates the optimal route.
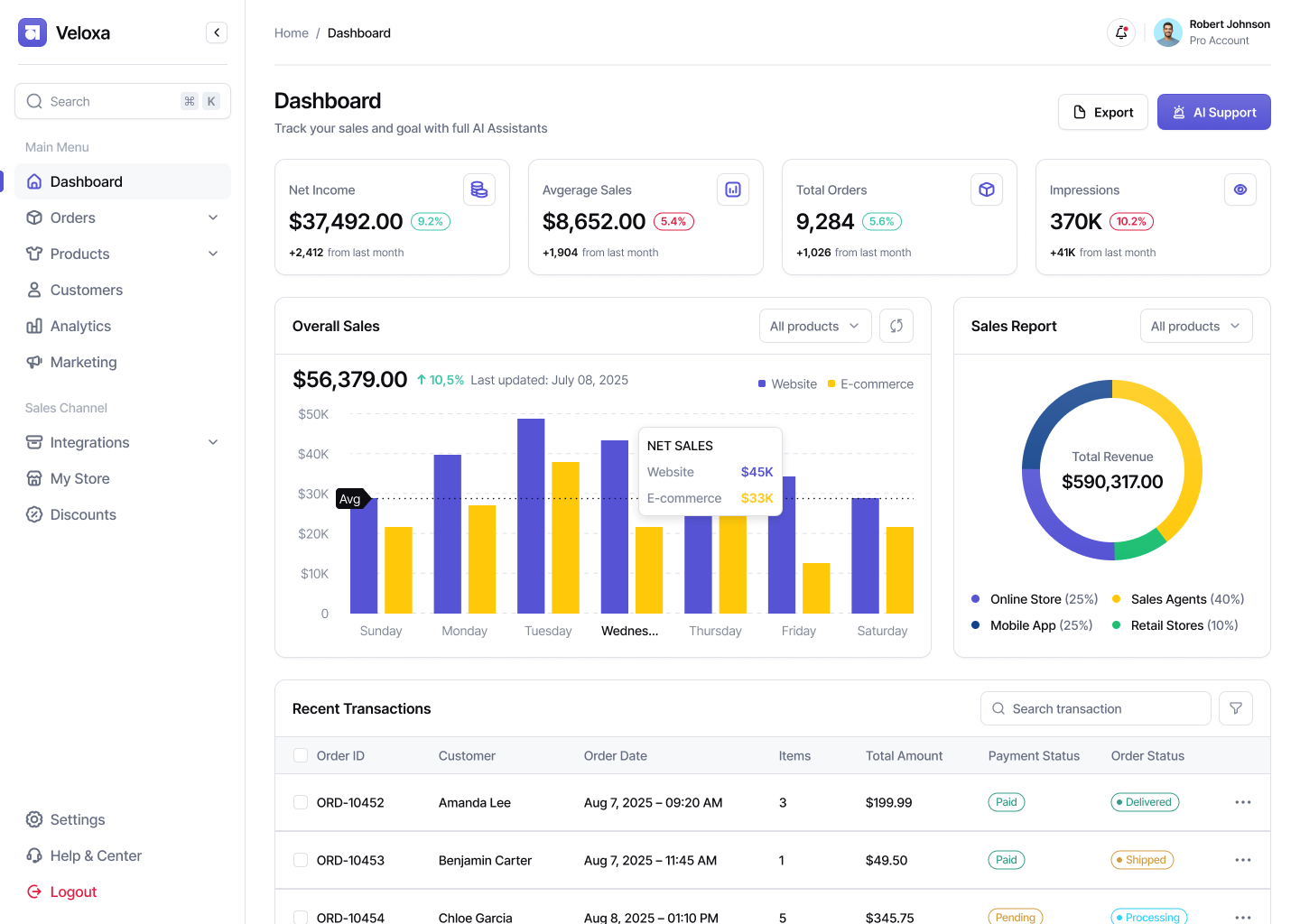
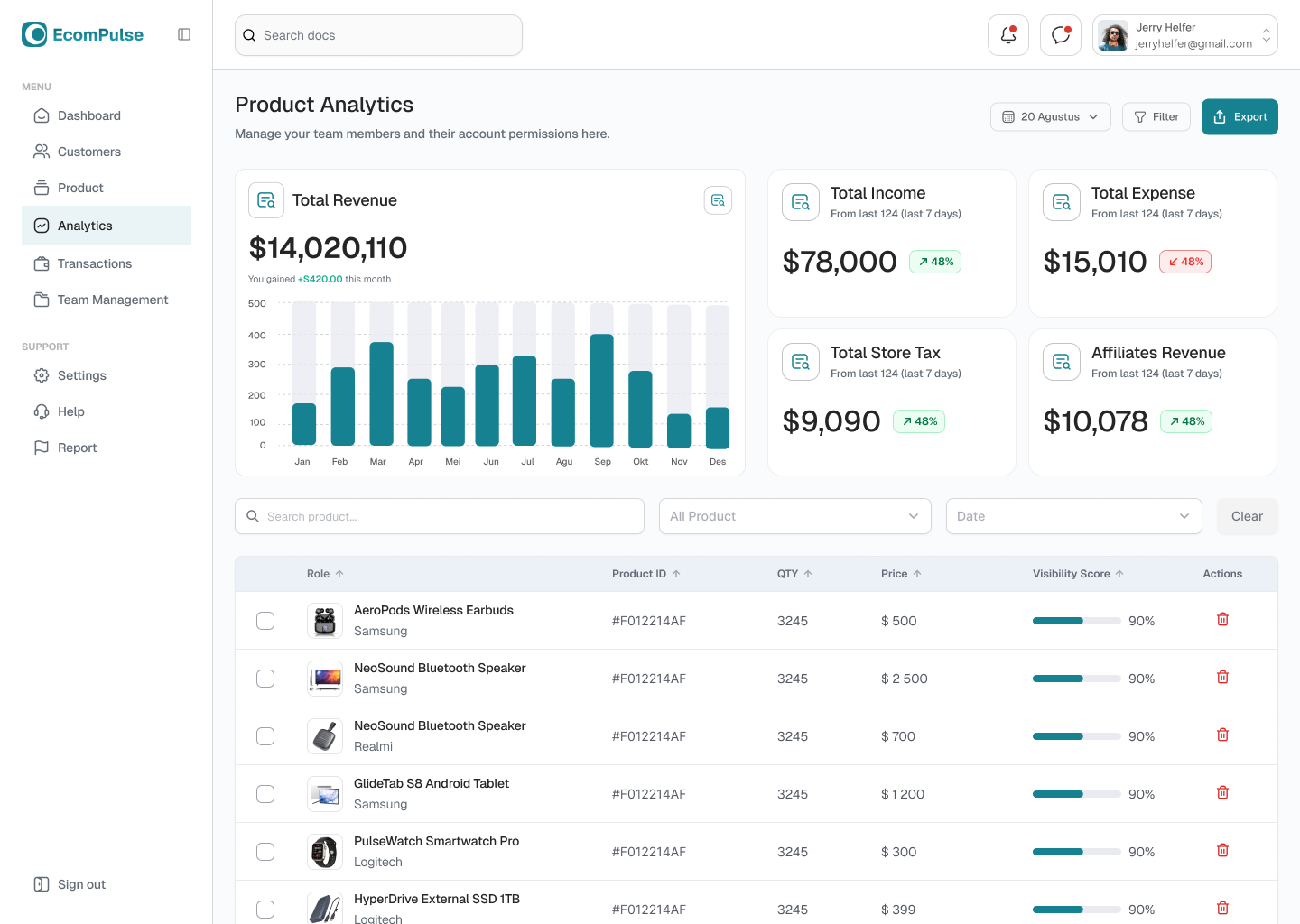
BI and Production Analytics:
- dashboards for management and line managers;
- deep statistics for each workshop, shift, employee;
- AI/ML modules for forecasting based on historical data;
- analysis of bottlenecks and inefficiencies;
- reports on profit, defects, equipment loading.
For example, in a CRM system for a foundry, management notices an increase in defects in one area on a dashboard displaying monthly defect indicators and initiates an audit.
The selection of the necessary program modules for production depends on:
- specifics of the production process – serial, custom, continuous production;
- size of the enterprise – small, medium, large.
- industries – mechanical engineering, food industry, light industry, etc.;
- current problems and goals of automation.
Stages of developing a CRM system for production management
Implementing a CRM system for manufacturing is a comprehensive and sequential process. Each stage plays a vital role in creating a functional and reliable product.
Business and Goal Analysis
The first stage involves analyzing the company's business processes. Problem areas, bottlenecks, and production needs are identified: which processes can be automated, what data needs to be collected, and what tasks the system should address. The analysis also includes market research, competitor analysis, and identification of necessary integrations with other systems.
Technical specifications
Based on the analysis, a technical specification is created – a document outlining the requirements for the future CRM system for an industrial enterprise, including features, integrations, security, and scalability. The technical specification serves as the foundation for further development and helps create a program that fully meets the client's needs.
Prototyping
At this stage, the system's logical structure is created, user scenario diagrams are developed, and modules and their interactions are designed. Next, interactive interface prototypes are created, allowing for a visual assessment of the system's usability. Integrated production management systems will operate under high load conditions, so it's important for users to quickly navigate the system.
UX/UI design development
A user-friendly and intuitive interface is a crucial element of any CRM. Designers must consider the specifics of manufacturing operations: operators, managers, logisticians, and other employees must be able to easily find the functions they need and work without delays. UX/UI designers use modern tools such as Figma, Adobe XD, and Sketch, which enable the creation of responsive interfaces.
Creating a program code
At this stage, programmers bring the project to life. For the client-side (frontend), they use React, Angular, or Vue.js, providing a user-friendly and fast interface. The server-side is implemented using Python, Node.js, or PHP, which allow for processing large volumes of data and efficient interaction with databases. Integrations with necessary services are implemented via APIs.
Testing
QA engineers conduct multi-stage testing to identify errors, verify the correct operation of all modules, and ensure data security. It's important to test the system's stability under high loads, as production CRM systems must process large amounts of data in real time.
Release and user training
Following successful testing, the system is transferred to the customer's server or hosted in cloud storage and deployed into production. This phase includes staff training, data transfer from existing systems, integration setup, and initial reporting configuration. Our specialists ensure a phased implementation of the CRM system across the enterprise to avoid disrupting ongoing processes.
Project support and development
Once implemented, CRM requires maintenance and development. Technical support for a production management system includes software performance analysis, regular updates, functionality improvements, and the integration of new technologies – for example, AI and machine learning for demand forecasting and resource optimization.
Why is it better to order a CRM for manufacturing rather than buy a ready-made solution?
Off-the-shelf production management software is versatile, but it can't fully meet the specific needs of a manufacturing business. Only by ordering a custom development can you create a tool that fully aligns with your company's processes, structure, and goals.
Why is it worth ordering the development of a management system for your enterprise rather than purchasing a ready-made program?
- Universal software products contain template functions, funnels and stages, but in a manufacturing enterprise, each process is specific;
- your own CRM can be easily adapted when changing your business model, expanding production, or launching new lines;
- A unique CRM system for manufacturing can directly interact with production equipment, accounting systems, payments, and logistics modules;
- Ready-made solutions are usually hosted in the cloud and do not provide full control over information storage, while custom development allows you to implement CRM on your own servers;
- In a custom system, the user interface is designed for the tasks of specific employees: technologists, logisticians, suppliers, and foremen;
- Ready-made solutions are often overloaded with features that are not used but for which you have to pay, while a custom CRM system for production contains only the necessary modules.
Why you should order CRM development for manufacturing from AvadaCRM
Manufacturing companies are always facing unprecedented challenges. If your business faces difficulties managing orders, logistics, warehouses, or personnel, or requires cost optimization, flexibility, and responsiveness, it's time to go digital.
AvadaCRM has been providing custom CRM system development services for businesses of all sizes and industries for over 10 years. We'll help you create an intelligent platform that not only streamlines your production processes but also takes your business to a new level of efficiency, minimizes risks, and increases profitability.
FAQ
-
How does CRM for manufacturing differ from ERP systems?
A CRM system is focused on managing relationships with customers, suppliers, and contractors, as well as automating processes. An ERP system is more focused on enterprise resource planning, including accounting, finance, and inventory management.
-
Can a manufacturing CRM system receive equipment data?
Custom industrial control systems synchronize with IoT devices, CNC machines, and other monitoring systems. This enables real-time data collection on equipment status, predictive maintenance, and downtime prevention.
-
How does CRM help in product quality management?
CRM makes production easier to control, as the program records data on each batch of products, tracks production stages, and stores data on quality inspections and customer complaints. This helps quickly identify and resolve defects, as well as improve production processes.
-
Is CRM production management suitable for remote departments?
Cloud CRM systems allow you to centrally manage multiple factories or production sites, receive operational reports, and coordinate staff work.
-
Is CRM suitable for small businesses?
A customized CRM for a factory can be scaled to meet any business needs. Small businesses can use basic functions for order and inventory management, and then implement additional modules as they grow.
-
Is it possible to configure a CRM to work with both B2B and B2C simultaneously?
Automated production planning and management systems support both models. For B2B, this includes long-term contract and partner management, while for B2C, it includes order automation, customer interaction, and marketing tools.
-
What tasks does production automation take on (examples)?
In metallurgy, CRM helps analyze productivity, and in clothing production, it helps manage fabric batches and distribute orders between workshops.
-
How much do custom automated manufacturing execution systems cost?
Development costs depend on the scale of the enterprise, the number of integrations with other systems, and the specifics of production processes. A simple CRM for basic processes requires less time and resources than complex custom solutions.
-
How long does it take to develop and implement a CRM system for manufacturing?
The development time for a customized production management system is four months. Ready-made solutions can be implemented more quickly, but they will need to be adapted to the company's business processes, which requires additional costs, downtime, and time.
-
Is it possible to integrate with production equipment (scales, scanners, machines)?
Yes, we can integrate with equipment via APIs, OPC servers, or other protocols, allowing the system to receive and process data from scales, data collection terminals, barcode scanners, PLC controllers, etc.