

Odoo
Solutions
When a business needs a unified management system without the time-consuming and costly development of its own ERP, it makes sense to consider implementing Odoo. The platform provides a ready-made functional foundation that can be adapted to a company’s specific processes while maintaining flexibility and control over system development.
At AvadaCRM, Odoo implementation is treated as an engineering and consulting project rather than a simple software installation. The objective is to design an ERP architecture that accurately reflects real business processes, supports scalability, and maintains manageability as the business grows.
What is Odoo
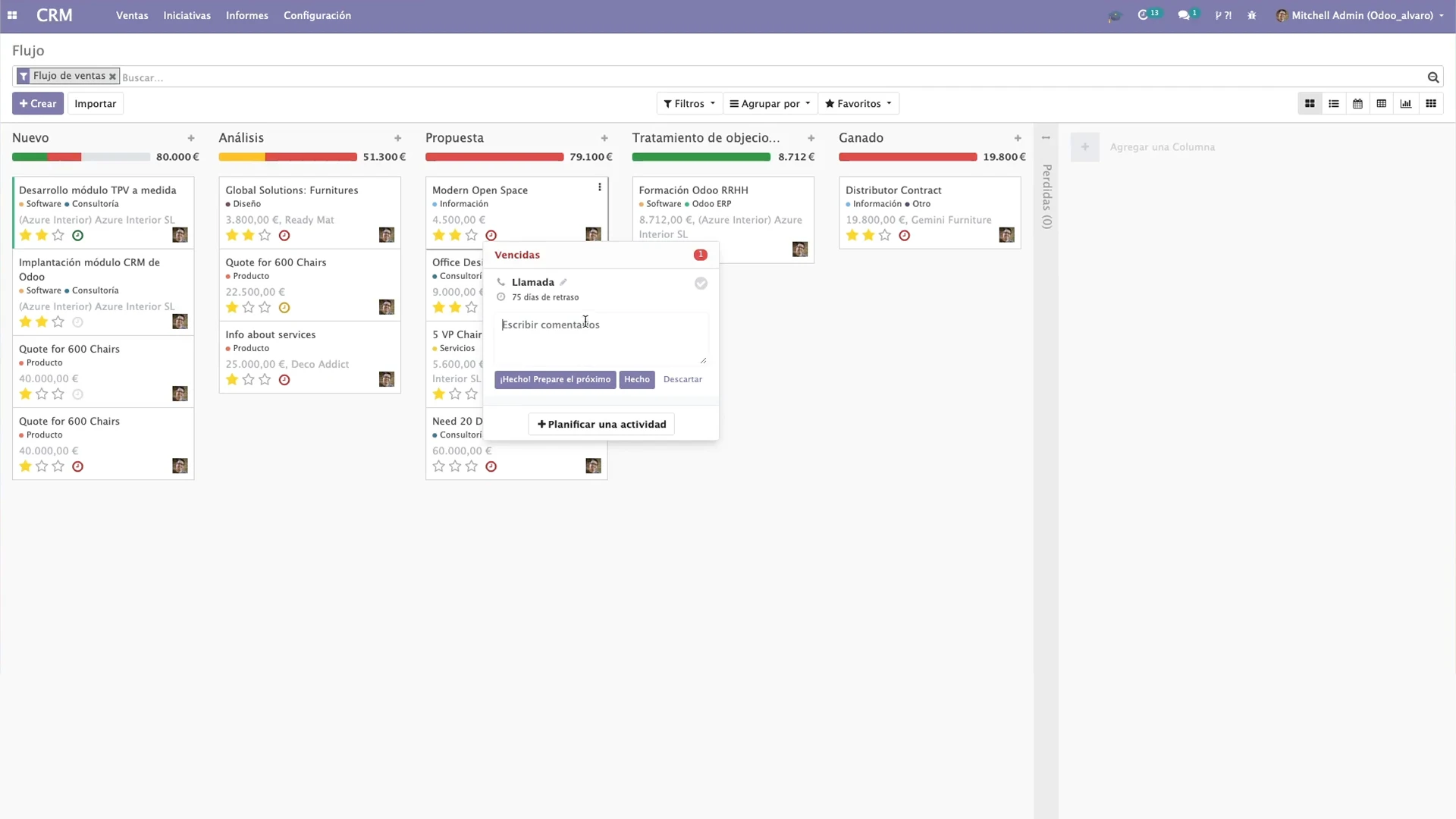
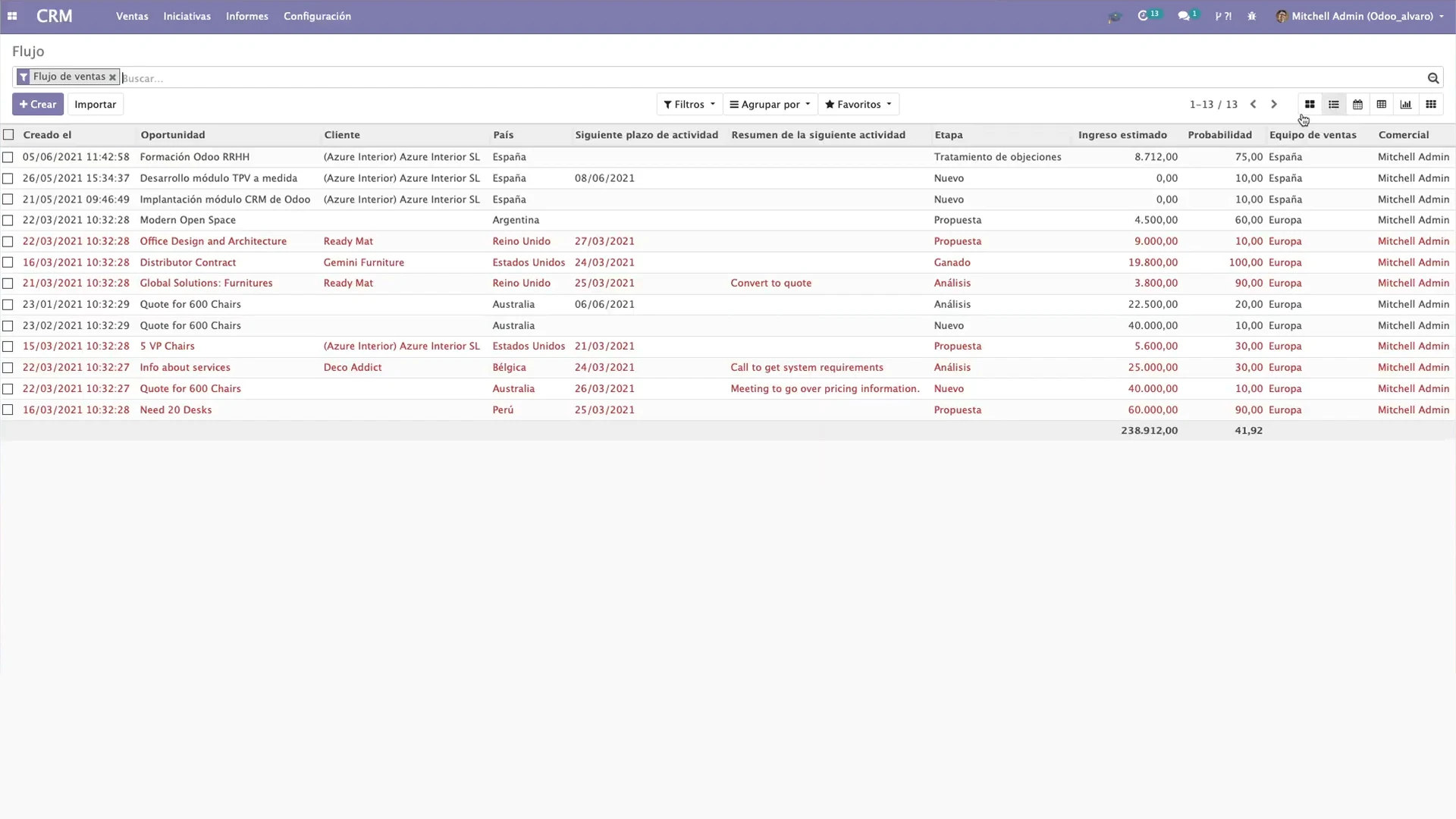
Odoo is a modular ERP system with open-source code and a single centralized database. Within one platform, it combines sales, CRM, finance, purchasing, warehouse management, manufacturing, HR, and online channels.
- Odoo as a modular ERP
Each business process is implemented as a separate module. Only the required applications are connected. The system scales without “rebuilding” the core.
- Unified database
All departments work within a single environment. Orders, payments, and warehouse movements are transactionally linked, without manual data transfer.
- Connection between business processes
CRM, purchasing, warehouse, accounting, and manufacturing are connected through end-to-end workflows – from lead to closing documents.
- No data duplication
Data is entered once and reused across the entire system. This reduces errors and increases accounting transparency.
Who Odoo implementation is suitable for and what problems it solves
The system is ideal for companies that want to move away from fragmented software solutions and adopt a unified management tool without building their own system from scratch.
- Scalable businesses – Odoo allows easy connection of modules, users, and warehouses as the company grows, without restructuring the system.
- Companies with multiple departments – All departments are unified in a single database with automatic transfer of up-to-date data.
- Businesses with warehouses or manufacturing – Provides accurate real-time tracking of inventory, batches, cost of goods, and production.
- For control and transparency – Delivers complete analytics on finance, tasks, and profitability without manual reporting.
- Odoo is widely used in retail and wholesale trade, e-commerce, distribution, logistics, and both mass and custom manufacturing.
- The system is also suitable for IT companies, consulting, construction, HoReCa (restaurants, cafés, hotels), medical and educational centers, with the ability to adapt to specific business processes.
Implementation stages
Odoo implementation is a full-scale business process transformation project, not just software installation. The system is open and flexible, which requires adaptation to real business needs.
Each stage represents a transition from analysis to a working system, with a focus on real business requirements.
- Audit and requirements – Analysis of business processes, identification of bottlenecks, and formulation of requirements for automation, reporting, and integrations.
- Design – Definition of system architecture, modules, data flows, access rights, timelines, and budget.
- Configuration and customization – Adapting Odoo to business processes, adding automation and reports with minimal custom development.
- Integrations – Connecting banks, payment systems, marketplaces, delivery services, telephony, and other systems for unified data exchange.
- Testing – Verifying system performance across all key scenarios until full stability is achieved.
- Training – Training employees by roles to ensure confident system usage.
- Support and development – Supporting the system after launch and scaling it together with the business.
Odoo ERP implementation typically requires a team of 3-6 specialists: a business analyst, Odoo developers, a QA specialist, and a project manager. For large projects, DevOps specialists are also involved.
The system can run in the cloud (Odoo.sh, AWS, Google Cloud) or on-premise on the company’s own servers.
Technologies used include: Python (server-side logic), PostgreSQL (database), JavaScript (web interface), Docker, and Nginx (deployment and infrastructure).
The interface is fully responsive for mobile devices, and official applications are available for Android and iOS.
Odoo Modules and Their Role in Business
Odoo is built on a modular architecture: modules are connected as needed and operate within a single database, ensuring end-to-end data usage without duplication.
Website and Online Sales
- Website – creation of corporate websites, landing pages, and content pages with ERP integration.
- E-commerce – online sales with automated order processing, payments, and delivery.
- Blog – publishing articles and content for marketing and SEO.
- Forum – building a community and supporting user interaction.
- Live Chat – real-time communication with website visitors and customers.
- E-learning – creation of courses, tests, and training programs.
Sales and Customer Management
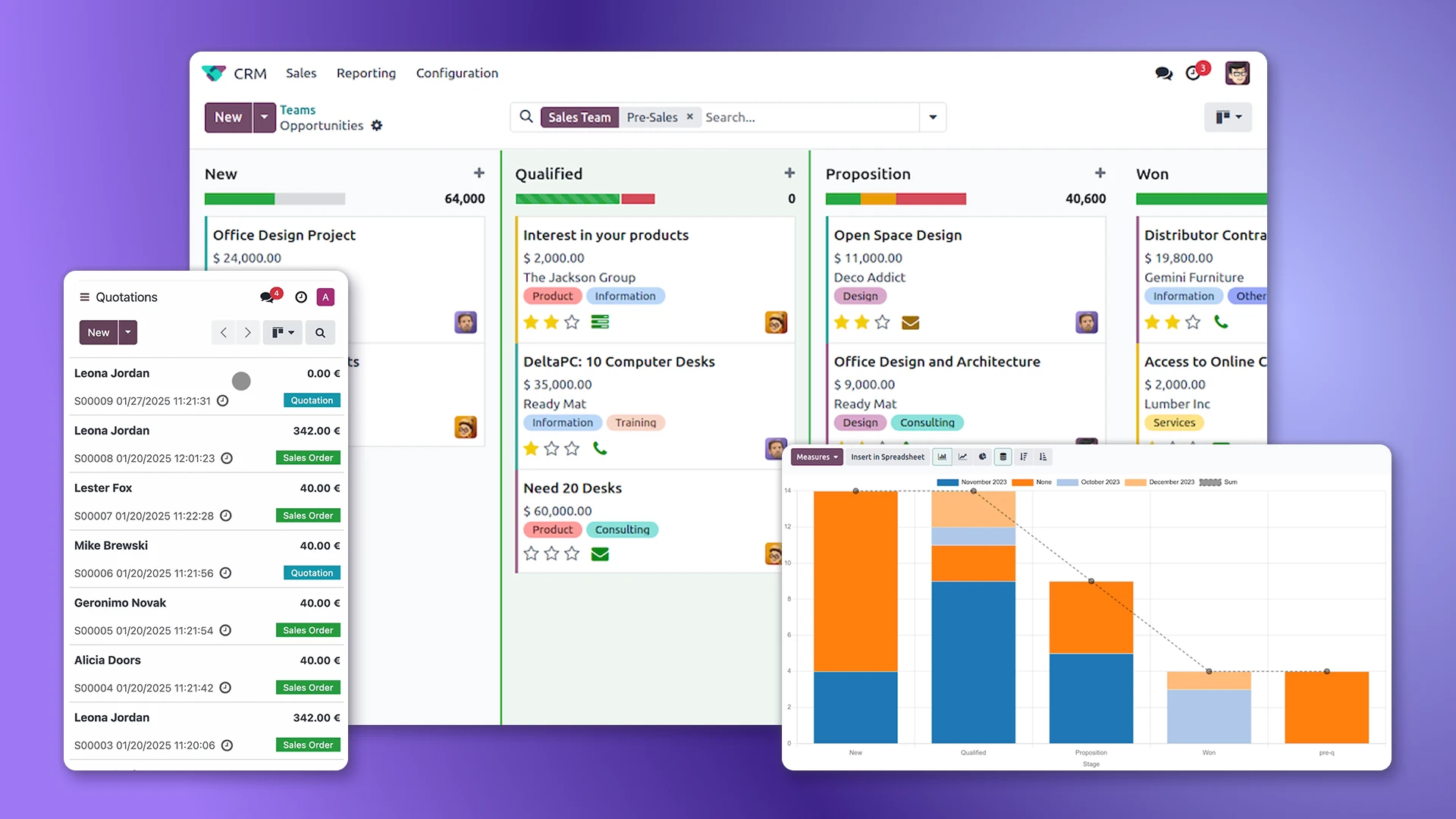
- CRM – management of leads, sales pipeline, and customer communications.
- Sales – quotations, orders, invoices, and deal control.
- Point of Sale (POS) – retail sales with support for POS hardware.
- Restaurant POS – management of orders, tables, and kitchen operations for hospitality.
- Subscriptions – management of recurring payments and contracts.
- Rental – tracking and control of equipment and asset rentals.
Finance and Document Management
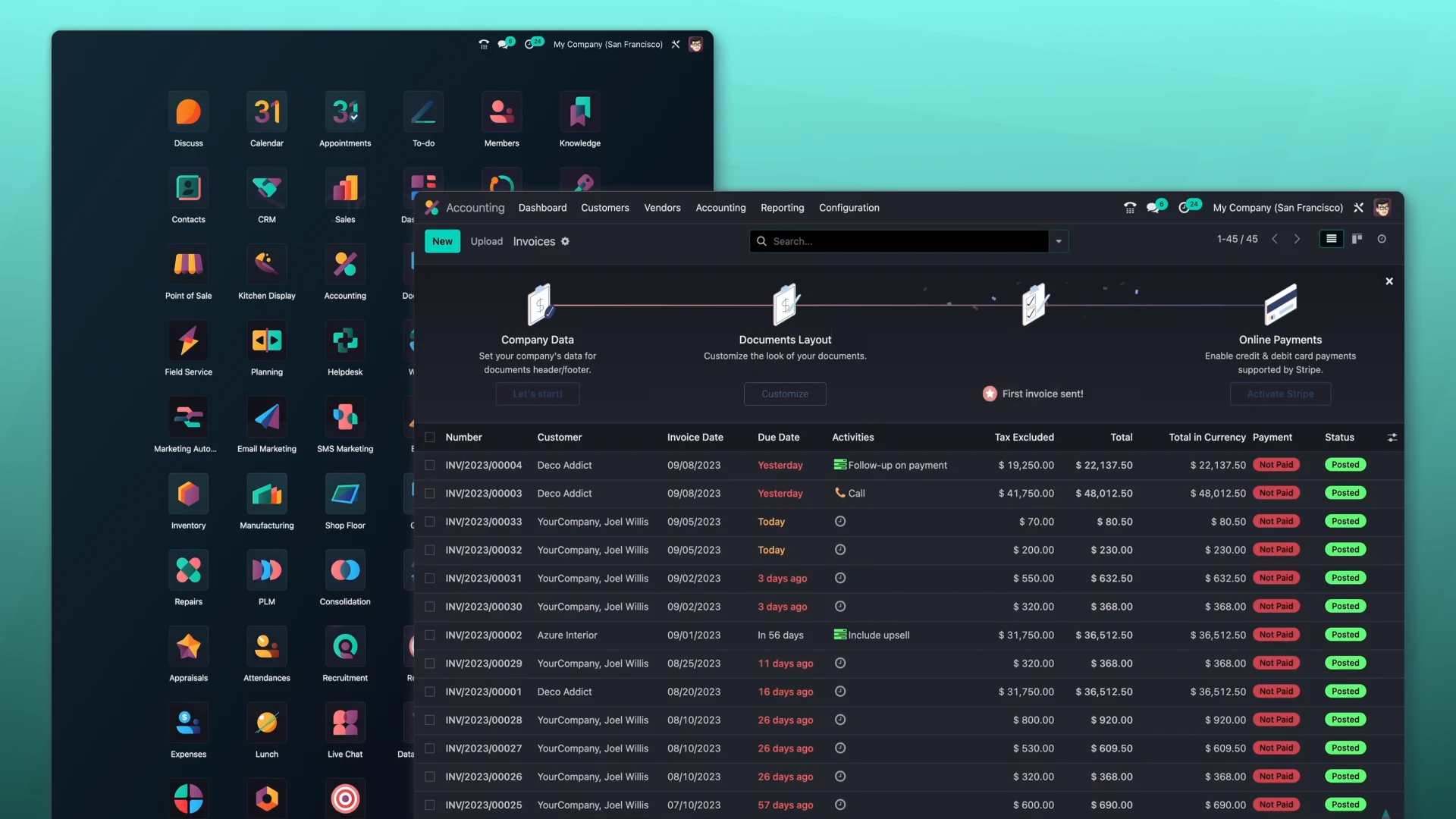
- Accounting – financial accounting, reporting, and control of income and expenses.
- Invoicing – creation and sending of invoices to customers.
- Expenses – tracking and control of corporate expenses.
- Documents – centralized storage and document management.
- Electronic Signature – online document signing within the system.
- Spreadsheets – data analysis and reporting in spreadsheet format.
Inventory, Purchasing, and Manufacturing
- Inventory – real-time tracking of stock levels, movements, and inventory counts.
- Purchasing – management of supplier orders and deliveries.
- Manufacturing (MRP) – planning and control of manufacturing orders and bills of materials.
- PLM – product lifecycle management and technical documentation.
- Quality Control – inspections and quality checks for products and processes.
- Maintenance – planning and tracking of equipment maintenance.
Human Resources (HR)
- Employees – management of employee data and organizational structure.
- Recruitment v hiring and recruitment process management.
- Time Off – planning and tracking of vacations and absences.
- Employee Appraisals – performance evaluation and employee reviews.
- Referrals – internal recruitment and incentive programs.
- Fleet – management and tracking of company vehicles.
Marketing
- Marketing Automation – setup of marketing scenarios and funnels.
- Email Marketing – email campaigns and performance analytics.
- SMS Marketing – bulk SMS notifications and communications.
- Social Media Marketing – publishing and monitoring activity across social channels.
- Events – event organization and participant registration.
- Surveys – collection of feedback from customers and employees.
Services and Projects
- Projects – management of projects, tasks, and stages.
- Timesheets – tracking time spent on tasks and projects.
- Field Service – planning and control of on-site service operations.
- Helpdesk – handling customer requests and support tickets.
- Planning – management of employee and resource utilization.
- Appointments – online booking and schedule management.
Productivity and Communications
- Discuss – internal corporate chat and notifications.
- Approvals – management of approval workflows.
- VoIP – calling and telephony integration with CRM.
- Knowledge Base – storage and structuring of internal information.
- IoT – integration with devices and equipment.
Odoo Customization for Non-Standard Business Processes
Odoo’s standard functionality covers most typical business needs. For companies with unique processes, the system can be customized by carefully adapting it to specific requirements while minimizing custom code to ensure stable and secure updates.
What We Can Improve in Odoo
Workflows. Configuration of document flows with conditions, statuses, approvals, and notifications, automating transitions between stages and eliminating manual task handoffs.
Process Automation. Implementation of automated actions based on events and triggers: creation of related documents, status changes, notifications, and запуск of manufacturing and warehouse operations.
Custom Fields and Forms. Extension of customer, product, project, and document records to reflect business-specific requirements.
Business Rules and Constraints. Implementation of rules that control system logic, including discounts, limits, blocks, mandatory checks, and approval conditions.
Reports and Dashboards. Enhancement of standard reports and creation of management dashboards tailored to roles and KPIs: sales, profit, accounts receivable, and employee performance.
Odoo Integrations with External Systems
Odoo can be integrated with external services and systems via APIs and ready-made connectors, enabling end-to-end data exchange and process automation.
Systems Most Commonly Integrated:
- Websites and e-commerce platforms – orders and inquiries automatically flow into CRM and inventory.
- Payment systems – payments automatically update order statuses and are reflected in financial records.
- Telephony – calls are logged in CRM, and customer records open automatically.
- Corporate email – correspondence is linked to customers and deals.
- Messengers – chats are handled and stored directly within Odoo.
- Accounting systems – synchronization of partners, documents, payments, and balances.
Common Mistakes in Odoo Implementation
Odoo implementation is a business process transformation, not a technical installation. In practice, the following mistakes are most common:
- Lack of pre-project analysis – the system is implemented without understanding real processes and bottlenecks.
- Transferring outdated processes – mechanical replication of legacy system logic reduces the effectiveness of Odoo automation.
- Excessive customization – complex custom developments complicate system support and updates.
What Businesses Gain from Proper Odoo Implementation
- Reduced operational costs – less manual work, fewer errors, and no data duplication.
- Faster management decisions – up-to-date metrics available at any time, without waiting for reports.
- Predictability and control – processes run according to defined rules, with deviations visible immediately.
- Growth without chaos – the business scales without losing manageability or sharply increasing costs.
Support and Ongoing Development After Implementation
After launch, the system should be supported and developed alongside the business.
The AvadaCRM team can provide Odoo support as needed, ensuring stable system operation, up-to-date updates, and advisory support for further development.
Support includes:
- secure updates and system monitoring;
- adaptation to company growth;
- adding new automations, reports, and configurations without downtime;
- user consultations and training as required.
Odoo Implementation by AvadaCRM
If you are considering transitioning to a unified ERP system or evaluating Odoo as a potential solution, the first step is to discuss the system architecture, module set, and integrations, taking into account your current business processes, industry specifics, and growth plans.
High-quality implementation does not start with installation, but with understanding the real operational landscape. Therefore, the first and key stage is an online consultation and audit of current business processes: reviewing the core functions of the future system and identifying points of time, data, and resource loss.
Our team has solid experience working with complex and non-standard cases, including:
- manufacturing with bills of materials, multi-level planning, and accurate cost calculation;
- distribution and wholesale operations with multiple warehouses, branches, and multi-company structures;
- retail and HoReCa with POS integration, online stores, and inventory management.
We are ready to discuss your project and propose a technically sound solution.
FAQ
-
Can Odoo be implemented in stages?
Yes. Implementation typically starts with core modules such as CRM, Sales, and Inventory. Manufacturing, Finance, and HR are then added as needed.
-
What is the difference between Odoo Enterprise and Community?
Community is the free version with basic functionality. Enterprise is the commercial version that includes mobile applications, Odoo Studio for no-code customization, advanced analytics, official support, and regular updates.
-
How long does Odoo implementation take?
Timelines depend on the scope and complexity of the project. A basic module set is usually implemented within 3-4 months, mid-sized projects take 4-8 months, and complex implementations with integrations can take 8-14 months. A phased rollout is often used.
-
Is Odoo suitable for medium and large businesses?
Yes. Odoo is used by companies with 50 to 500+ employees. For large organizations, the Enterprise version and scalable infrastructure are recommended.
-
Can you start with a basic setup and expand the system over time?
Yes. New modules can be added without changing the database structure and will immediately work with existing data.
-
How complex is Odoo customization?
Standard customizations are handled using Odoo Studio. More advanced changes require development in Python, XML, and JavaScript.
-
Who provides support after go-live?
Support can be provided by your internal team, an implementation partner, or Odoo itself (Enterprise version). In practice, a hybrid support model is commonly used.